CBC or Complete Blood Count is one of the basic blood tests done to determine the quantitative and qualitative components of the cells in the blood. The CBC now performed completely by automatic standard machines. If any abnormalities detected then the reference to pathologist required to investigate further.
These tests may take from a few seconds to minutes and the standard report consists of over 15 parameters. These parameters explained in detail, keeping in mind an average healthy adult. This article is not a substitute for medical advice.
CBC Blood Parameters explained
HGB – Haemoglobin in CBC
Haemoglobin is a protein present on the red blood cells. Also it is the main protein which carries oxygen from the lungs to the body. Any abnormality in haemoglobin would result in serious consequences. Raised haemoglobin levels are due to the compensatory mechanism for a low oxygen level.
Most common reasons are living on a high altitude or smoking. A low haemoglobin may associated with disease or other conditions. For dental procedure a Hgb level less than 10 mg/dl should investigated further by a local physician.
Normal: 11- 16 mg/dl (female) & 13 – 16.5 mg/dl (male)
RBC – Red Blood Cell Count
Red blood cells are the corpuscles which contain the haemoglobin and carry oxygen throughout the body. A low RBC would indicate a vitamin or iron deficiency. It could also be due to malnutrition or kidney disease. A high RBC would indicate some kind of a compensatory mechanism due to low oxygen carrying capacity, similar to a high haemoglobin levels. The other reason could be certain bone marrow disorders.
Normal: 4.5 – 5.5 millions/mm3

WBC – White Blood Cell Count in CBC
A white blood cell count is the test that measures the number of white blood cells in your body. They the main defence cells of the body. This count increases in case of an active infection. A higher WBC would indicate that the body is fighting an infection or some pathology or allergy. Immediate increase of WBC after the dental treatment expected, as a bodies defence mechanism.
Normal: 4000 – 10000 cells/mm3
Platelet Count CBC
A platelet blood count is a blood test that measures thee average number of platelets in the blood. A low platelet count would indicate that the clotting mechanism hampered. A high platelet count could be a result of the abnormality in bone marrow.
Normal: 150000 – 410000 /mm3
MCV – Mean Corpuscular Volume
This test measures the average size of the red blood cell. A low MCV value indicates a small red blood cell which could result in abnormal bruising or bleeding, fatigue, pale skin. They are important to diagnose medical conditions like anaemia and thalassemia. A greater level of MCV could be due to B12 or folic acid deficiency or liver disorder or hypothyroidism.
Normal: 83 – 101 fl
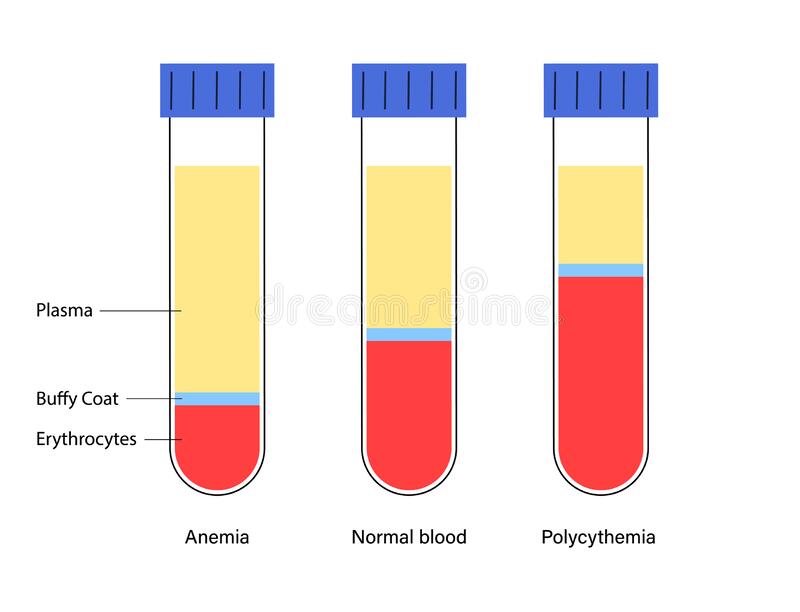
HCT – Haematocrit
This test measures the percentage of red blood cells in the total blood volume. A low haematocrit level may be a sign of bone marrow disease, inflammatory ideas, iron and vitamin deficiency, Internal bleeding, haemolytic anaemia, kidney failure, leukaemia, lymphoma, sickle cell anaemia. Whereas a high haematocrit could be a sign of heart disease, dehydration, kidney and lung disorder, or if you live in a higher altitude.
Normal: 40 – 50 %
MCH – Mean Corpuscular Haemoglobin
This test gives the average amount of haemoglobin in the blood cells. The amount of haemoglobin in a red blood cells. This test gives an indication of iron deficiency anaemia or a vitamin deficiency. Low count may indicate iron deficiency and high count may indicate larger red blood cells due to vitamin deficiency. Normal: 27 – 32 pg
MCHC – Mean Corpuscular Haemoglobin Concentration
It is similar to MCH but instead of per cell it is the value for a group of cells. This represents a more normalised value. A vast proportional difference in the 2 could be indicate of abnormal cell architecture. Normal: 32 – 35 g/dl
RDW-CV and RDW – SD – Red Cell Distribution Width
It is the variation between the width of the red blood cells. A higher value indicates that the width difference between the red cells is quite large. A large RDW can tip the doctor off about vitamin or nutrient deficiency or anaemia. The difference between CV and SD is of a mathematical calculation. Normal: 11.6 – 14%
MPV – Mean Platelet Volume in CBC
This test gives the average size of the platelet in the blood. These test usually read with the platelet count. They play a role in stopping of blood in case of an injury.
A high MPV is an indication of larger platelets. A large platelet is a young platelet. So either the body producing platelets quickly and/or the old ones are getting destroyed faster. This then warrants additional investigation with bone marrow typing etc.
Other reasons for high MPV is hyperthyroidism, heart disease, diabetes, vitamin D deficiency, high blood pressure, stoke, atrial fibrillation. Whereas a low MPV could indicate inflammatory bowel disease, aplastic anaemia and chemotherapy.
PDW – Platelet Distribution Width
This test is an indicatory of the platelet activation. A higher PDW would indicate large width of the platelets. A large platelet is younger and also it could be due to activation of the platelet. It could be due to activation in an acute coronary event, internal bleeding or a bone marrow disorder.
PCT – Plateletcrit
Like haematocrit it is the total platelet mass in blood. Smoking and alcohol consumption along with physical activity may modify the platelet count. In case the PCT value is low it could be a sign of thrombocytopenia and may cause prolonged bleeding conditions.
P-LCR – Platelet larger cell ratio and P-LCC – Platelet large cell count
Platelet large cell ratio defined as the percentage of platelet that exceed the normal value of platelet volume. A high P LCR is indicative of thromboembolic ischemic event or a septic condition.
Lymphocytes % and absolute
They are one of the body’s main types of immune cells. An increased lymphocyte would indicate a bacterial infection.
Mid cells % and absolute
They correspond to the cells of the immune system which corresponds to the monocytes, and other macrophages. Any abnormalities warrant further investigation with a pathologist.
Granulocytes % and absolute
They are small granules of the white blood cells which include neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils.
CBC Overview: A complete blood count (CBC) is a blood test used to evaluate your overall health and detect a wide range of disorders, including anaemia, infection and leukaemia. A complete blood count test measures several components and features of your blood.
How is CBC test done?
The surest method is to visit a pathologist or a registered laboratory wherein the nurse of the lab tech will take a sample of the blood from the vein in your arm. This blood sample, then sent to the laboratory for processing. At Royal Dental Clinics, with our in-house fully automatic pathology machine the reports can prepared within a few minutes. Usually around 1 to 2 ml of blood required for a CBC test. But with the new advanced technology in analysers now a few drops of blood are enough to give accurate results.
In case of any discrepancy one should visit their pathologist or physician.





Excellent Service very good doctors and staff are very polite. and helpful.