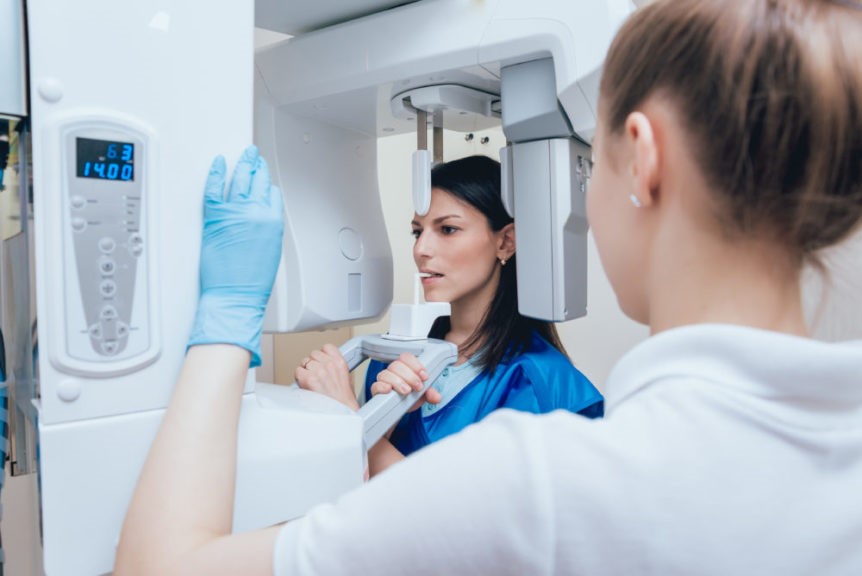
When you think about it, getting a cadaveric body scan may not seem like the most natural thing in the world. It’s an imaging technique usually used for anatomy research and medical diagnostics, after all. But when you also factor in that dentists recommend a CBCT scan instead of standard X-rays as the preferred method for detecting hidden cavities and other oral problems in patients, you realize it’s actually a pretty brilliant idea. If you think about it, getting a cadaveric body scan may not seem like the most natural thing in the world. That said, there are some challenges involved with getting your dentist to authorize a CT scan as part of your treatment plan. First and foremost of these challenges is what sort of pre-scan prep work needs to be done beforehand—specifically regarding body jewelry such as piercings or tattoos that could potentially interfere with imaging results.
What is a CBCT Scan?
A CBCT scan is a type of imaging scan that uses X-ray beams and computer processing to create 3D models of the patient’s teeth and oral cavity. This is in contrast to a standard (or conventional) X-ray, which creates a 2D image of the teeth and other relevant structures from a single, fixed perspective. CBCT scans are more accurate than conventional X-rays in most cases, making them the preferred method of imaging for a number of dental procedures.
For example, dentists often use CBCT scans to get a better visualization of the soft tissues inside the mouth and throat, such as the tongue and tonsils. This can help clarify certain findings and/or rule out possible conditions, such as inflammation in the tonsils and/or tongue, that could otherwise be misinterpreted as cavities. CBCT scans can also be used to create virtual models of a patient’s teeth. Followed by a specialized computer program to create a customized dental treatment plan based on the image results.
Body jewelry and CBCT Scans
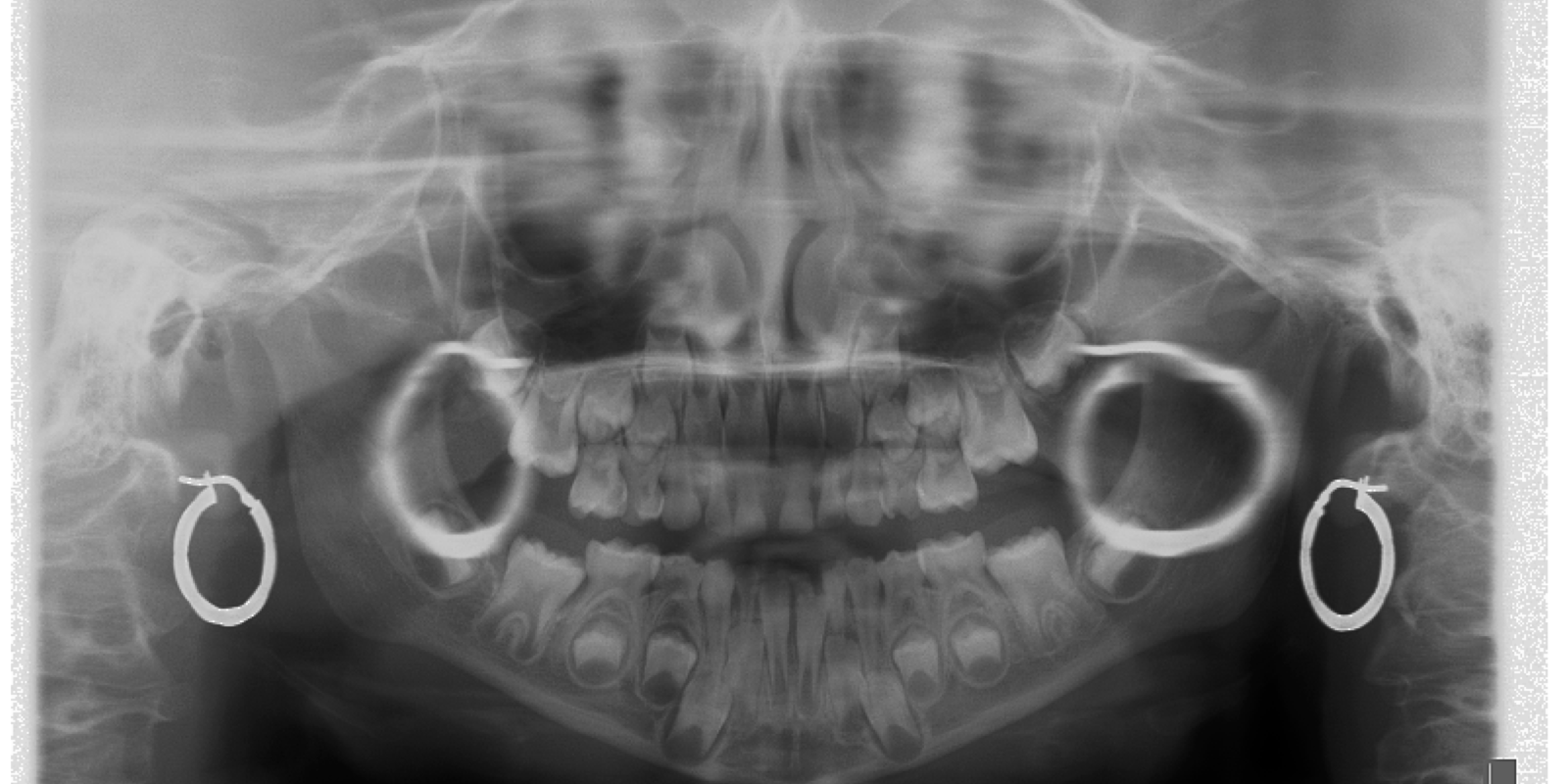
CBCT scans are usually safe for people with most types of piercings and body jewelry. With the exception of magnetic implants (such as a pacemaker) or implanted medical devices such as a diabetic monitor. If you are unsure whether or not you qualify for a CBCT scan. It’s a good idea to clear the procedure with your dentist, radiology facility, and/or medical doctor. It’s also a good idea to remove your body jewelry before going in for your CBCT scan.

Remember that CBCT scans use X-rays to create their images and that X-rays are electromagnetic waves (BMWs) that can be blocked by certain materials such as body jewelry. And since CBCT scans are more accurate than conventional X-rays. It’s important to be as careful as possible to avoid interference from body jewelry. This is especially true for piercings that are located in the oral region (such as on the tongue, lips, and/or gums), which could potentially obscure the image of a real cavity.
Does body jewelry have to be removed for a CBCT scan?
No, it does not have to be removed for a CBCT scan. However, if there is a chance that it could interfere with imaging results, the dentist might ask you to remove your body jewelry before going under the scanner. CBCT scans use X-rays to create images of the teeth and oral cavity. Which means that they can be blocked by certain materials. This means that it is important to avoid interference from body jewelry like piercings that could obscure the image of a real cavity.
However, it is generally safe to keep your piercings in place while having a CBCT scan. If you are concerned that your piercings may interfere with the results of your CBCT scan. It is a good idea to speak with your dentist about any concerns you have. Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing to your exam. You may be given a gown to wear during the scan. Metal objects including jewellery, eyeglasses, dentures and hairpins may affect the CT images and should be left at home or removed prior to your exam.
How do you determine whether to remove jewelry?
In most cases, you won’t need to remove your piercings for a CBCT scan. CBCT scans use X-rays to create images of the teeth and oral cavity. X-rays are electromagnetic waves that can be blocked by certain materials. Piercings are an example of a material that may interfere with the results of a CBCT scan. The oral region is the part of the body that is most likely to be affected by piercings. If your piercings are located in the oral region (such as on the tongue, lips, or gums), the X-rays may be blocked. This could obscure the image and lead to a mistaken diagnosis.
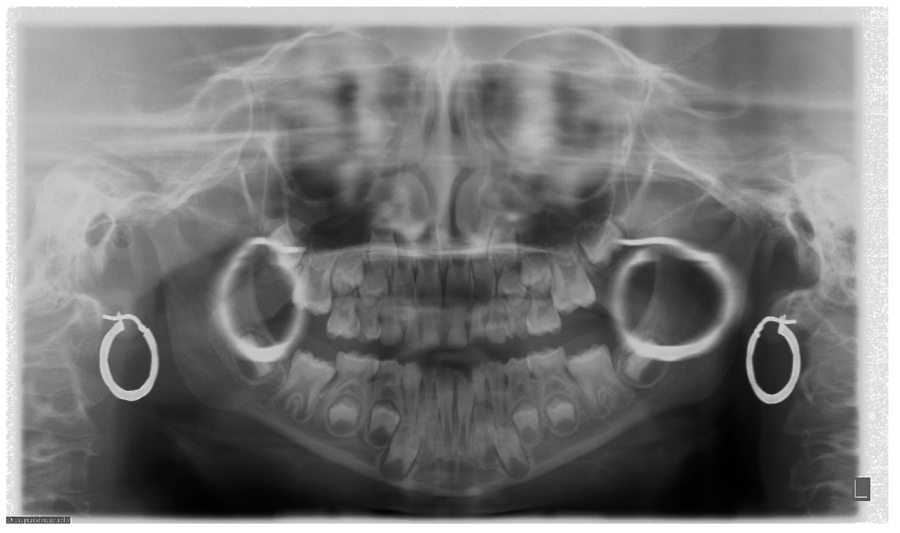
This is why dentists often advise patients with oral piercings to remove the jewelry before having a CBCT scan. However, it is generally safe to keep your piercings in place while having a CBCT scan. If you are concerned that your piercings may interfere with the results of your CBCT scan. It is a good idea to speak with your dentist about any concerns you have.
People with Body Jewellery Who Need a CBCT Scan
If you have oral piercings that may interfere with the results. Speak with your dentist about any concerns you have. They may recommend one of the following options as a way to reduce interference from your
- Piercings: Switch from oral to facial piercings. In some cases, oral piercings may interfere with the results of a CBCT scan. In these circumstances, switching to facial piercings is often a good solution.
- Use a lead shield during the CBCT scan: A lead shield is a device that protects the tissue that is sensitive to X-ray radiation during it. This reduces the risk of exposure to radiation while ensuring that proper imaging results are obtained.
- Change piercing type: In some cases, oral piercings may interfere with the results of a CBCT scan. In these circumstances, changing the type of piercing may be a good solution.
Conclusion
When you think about it, getting a cadaveric body scan may not seem like the most natural thing in the world. But when you also factor in that, they are more accurate than conventional X-rays. You realize it’s actually a pretty brilliant idea. It’s an imaging technique usually used for anatomy research and medical diagnostics, after all. Also removing any necklaces or other jewellery that are in the area that is being scanned is better.