Computerized tomography is an imaging technique that is used to see inside the body without making incisions. However, CT scans can have some limitations for patients who may be exposed to high radiation doses when undergoing it. Consequently, digital cone-beam computer tomography (CBCT dental scan) has been introduced as an alternative imaging technique in which a narrow beam of X-rays is used to scan the area of interest from many directions. The scattered X-ray photons are detected by a matrix of dozens of small photodetectors, called focal plane array (FPA). The information from these detectors is processed by a computer to reconstruct a 2D image from these low-resolution images taken from different angles.
What is the contraindication of CBCT?
The contraindication of CBCT is the reason why a patient cannot undergo CBCT. There are many contraindications of CBCT and they are as follows. The 3D dental scan is contraindicated in patients with an allergy to iodinated contrast material because it is an essential part of CBCT protocol. Similarly, CBCT is contraindicated in patients with an allergy to gadolinium (Gd), which is used to enhance the diagnostic quality of CBCT. If a patient is allergic to Gd, he/she must be treated with antihistamines to prevent allergic reactions.
A 3D scan with Gd is contraindicated in patients with a history of allergic reactions to Gd, as well as in patients with renal impairment. CBCT is contraindicated in patients who have coagulopathy, are pregnant, or are receiving anticoagulation therapy. A CBCT scan is also contraindicated in patients with a pacemaker or other implanted medical devices.
Risk of allergic reactions during a scan
There is a risk of an allergic reaction, particularly when patients are allergic to iodinated contrast material. CBCT scans are performed with iodinated contrast material, and allergic reactions are common. Patients who are allergic to iodinated contrast material must be treated with antihistamines to prevent allergic reactions. Allergic reactions may occur during or after the CBCT scan.
Reactions may include swelling and itching of the skin, hives, and difficulty breathing. If a reaction occurs, the CBCT scan must be stopped immediately. The patient must be given emergency treatment with epinephrine and steroids. Patients who are allergic to iodinated contrast material must be treated with antihistamines to prevent allergic reactions.
How do avoid the contraindication of CBCT?
Patients who have a contraindication of CBCT should be treated with alternative methods. Such as an X-ray imaging technique or an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) imaging technique. X-ray imaging is the simplest and least expensive imaging method. However, X-ray imaging may not be useful for the detection of some diseases, such as bone fractures and joint diseases. MRI is a high-resolution technique that is sensitive to the bone, soft tissues containing water, and blood-rich organs. Thus, MRI is useful for the detection of many diseases. However, MR imaging is more expensive than dental 3D scan.
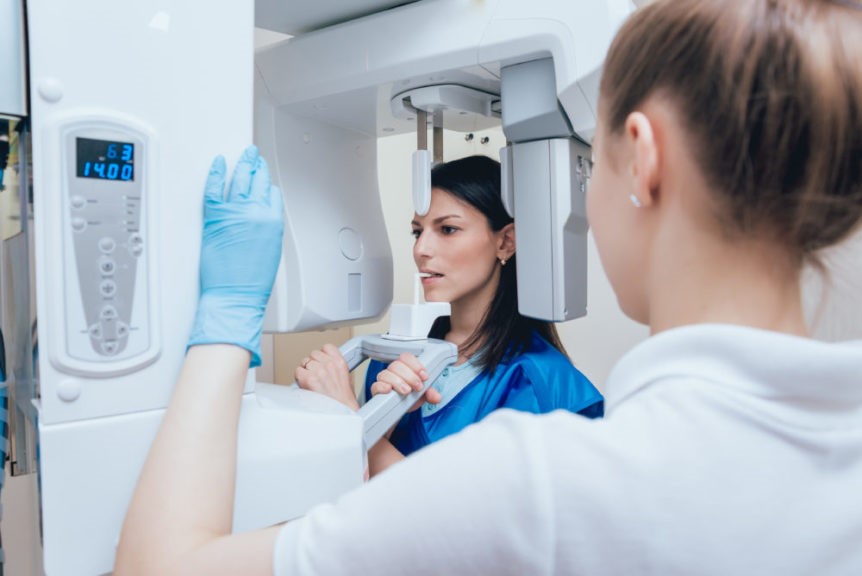

Limitation of CBCT in patients with metal objects
The limitation of CBCT in patients with metal objects is that they cannot be detected with CBCT. In the CBCT scan, a narrow beam of X-rays is passed through the body. If the beam encounters some metal objects, it is scattered and cannot be detected by the detector. Thus, there are blind areas in the CBCT image. Most commonly, bolts, screws, plates, and wires implanted in the body during surgery are detected by the CBCT image. Moreover, large metal objects located near the CBCT imaging area are also detected by the CBCT image.
For example, a calcium phosphate bone substitute may be detected by the 3D image because it is a weak scatterer and is not removed by the CT protocol. Thus, the limitation of CBCT in patients with metal objects is that large metal objects, such as plates and screws, cannot be detected by dental 3D scan. Therefore, these objects must be removed from the body by surgery before the CBCT scan is performed.
Patient benefits of CBCT scanning
- There are many benefits for patients undergoing a dental scan. Compared to regular X-rays, CBCT scans can better differentiate between many types of tissue. This includes bone, teeth, the IAN canal, and limited soft tissue. This increases the likelihood that practitioners will correctly identify pathology.
- Because fewer images are needed for diagnosis. Often just a single scan will provide accurate diagnostic information patients are properly diagnosed, triaged, and treated the first time. This reduces treatment ambiguity.
How do you explain this to patients?
- The average effective dose from background radiation is about 3 mSv per year. The adult effective dose from a CT exam of the abdomen is roughly equivalent to the adult effective dose from roughly 400 chest X-rays.
- The effective dose of CBCT exams varies depending on the volume of tissues being examined and the anatomical region being examined – the larger the field of view, the higher the radiation dose.
- Before performing 3D exams or purchasing a 3-D system, practitioners should select the most suitable volume size considering what clinical applications they expect the system to support. They should follow the guidelines provided by the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology and the European Academy of DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology regarding the limitations of the field of exposure
- CBCT units delivering the lowest doses are nearly equivalent to the dose of the panoramic exam, allowing dental professionals to benefit from the power of 3-D while limiting the risk associated with radiation exposure.
In addition, 3D systems using a smaller FOV have a higher image resolution in addition to lower doses. This increases the applications of CBCT to include endodontics, oral surgery, and orthodontics. Especially with units that combine 3-D imaging with panoramic/cephalometric imaging.
Conclusion
CBCT technique is an imaging modality that provides better imaging quality and reduced radiation dose compared with standard CTBT is an imaging technique that uses a narrow beam of X-rays to scan the area of interest from many directions. The scattered X-ray photons are detected by a matrix of dozens of small photodetectors, called an array detector or focal plane array. The information from these detectors is processed by a computer to reconstruct a 2D image from these low-resolution images taken from different angles.