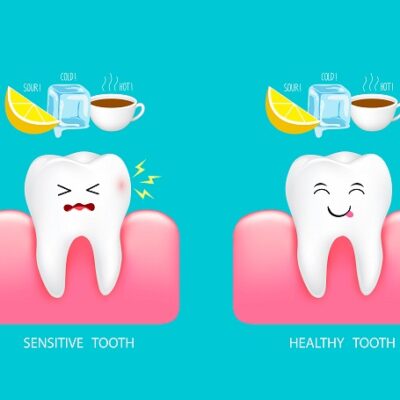
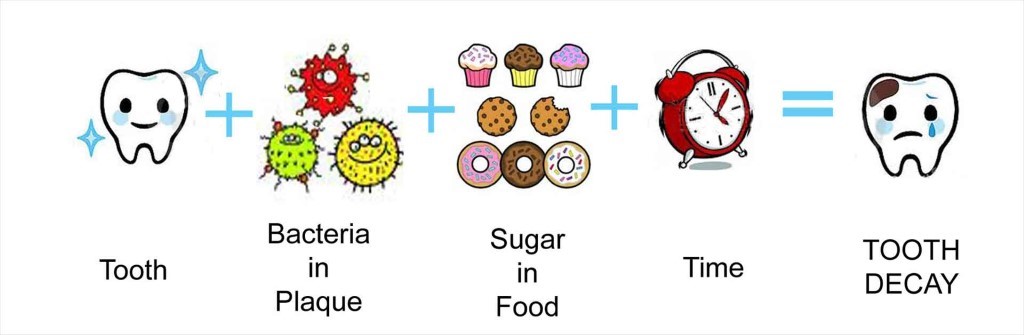
Your dental health is not just about avoiding cavities and bad breath. If Your oral health has a direct correlation with the health of your body, specifically the rest of your organs. Your mouth, nose, and throat are all connected in one way or another. They’re also filled with bacteria that love to call these places home. These small organisms (bacteria) live on almost every surface of our bodies, including our gums and tongue. There are billions of them living in these locations, each serving its own purpose as part of your body’s natural defense system against disease-causing germs. In this blog post, you will learn about the importance of good oral hygiene for systemic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart diseases, and how poor oral hygiene can lead to chronic conditions like periodontitis which can increase the risk of developing systemic diseases.
What is a systemic disease?
A systemic disease is a health condition that has an effect on more than one organ of the body. A lot of oral diseases such as periodontitis and caries, for example, can increase the risk of developing systemic diseases, such as diabetes and heart diseases. Systemic diseases are sometimes called chronic diseases because they can last for a long time. They are also long-term health conditions that can affect your body and its ability to work properly.
Because systemic disorders affect the entire body, the changes manifested in the appearance of the jaws in diagnostic images are usually generalised and often nonspecific, making it difficult to identify the diseases based on imaging characteristics alone.
Symptoms of systemic disease
A systemic disease is a disease that affects other parts of the body, or even the whole body. The hands are complex. They are composed of many types of tissue including blood vessels, nerves, skin and skin-related tissues, bones, and muscles/tendons/ligaments.
Systemic disorders can have gastrointestinal (GI) manifestations which are characterized by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, jaundice, and abnormal liver function tests. These gastrointestinal symptoms can be signs of various immunologic, infectious, and endocrine diseases.

Red streaks are an example of a systemic disease. Psoriasis is an example of a systemic disease. Pincer nail is an example of a systemic disease. Pyogenic granuloma is an example of a systemic disease.
✪ Change in size and shape of the bone.
✱ Change in the number, size, and orientation of trabecular.
✪ Altered thickness and density of cortical structures.
✱ Increase or decrease in overall bone density
✪ Changes in the first three elements can result in a decrease or increase in bone density.
Bone density
Because many parameters in the production of a diagnostic image influence the density of the image, it may be difficult to detect genuine changes in the density of bone. Systemic conditions that result in a decrease in bone density do not affect mature teeth; the image of the teeth may stand out with normal density against a generally radiolucent jaw.
In severe cases, the teeth may appear to lack any bony support. Also, cortical structures appear thin, are less defined, and occasionally disappear. A true increase in bone density may be detected by a loss of contrast of the inferior cortex of the mandible as the radiopacity of the cancellous bone approaches that of cortical bone. Often the radiolucent outline of the inferior alveolar nerve canal appears more distinct in contrast to the surrounding radiopaque dense bone.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD)
Cardiovascular diseases or CVD are a group of diseases that affect the heart and blood vessels. CVD affects more than a third of the global population, yet most people do not know that they have the disease. The risk factors for developing CVD include smoking, an unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, and higher levels of stress.
Poor oral health can be an indicator of other unhealthy lifestyle choices such as smoking, eating an unhealthy diet, or inadequate exercise. These factors can contribute to the development of CVD.

Chronic respiratory systemic diseases
There are many oral diseases that are closely linked with chronic respiratory diseases such as asthma and allergies. Some of the oral bacteria are found in high concentrations in the airway of people with asthma, allergies, or both. This means that these bacteria can cause inflammation and irritation in the airways, which can lead to more frequent asthma attacks, increased allergies, and other oral diseases such as periodontitis.
Poor oral hygiene is a key factor in the transmission of these diseases. There are a number of ways that oral diseases can affect the lungs. These include the transmission of bacteria from the mouth to the lungs. Increased production of sputum due to irritation and inflammation, and the transmission of bacteria from the teeth to the lungs after coughing.
Diabetes and complications with systemic disease
People with diabetes often experience more oral problems than others. Poor oral health can increase the risk of developing diabetes. This is due to the fact that certain oral diseases such as gum disease alter the way the body responds to glucose.
This leads to higher blood sugar levels and, over time, may increase the risk of developing diabetes. Good oral hygiene is important for preventing or slowing the progression of oral diseases. This means taking care of your teeth and gums by visiting your dentist regularly. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day, and using fluoride toothpaste.
Conclusion to systemic disease
Your oral health is more than just having a beautiful smile; it is a reflection of your overall health. This is why your dentist will always recommend that you maintain proper oral hygiene, such as brushing your teeth twice a day and visiting the dentist for regular cleanings and check-ups. Your dentist will offer advice based on the results of your oral examination and professional opinion on how you can improve your oral hygiene. Maintaining good oral hygiene is important for preventing or slowing the progression of oral diseases such as caries and periodontitis. This will also reduce the number of bacteria in your mouth and help you avoid transferring bacteria to other parts of your body.
Suggested Article –
Pros and Cons of Full Mouth Dental Implants
Difference between Crowns and Dental Implants?
Follow Us For More Updates