Dental infections can be very uncomfortable and painful, making it hard to eat or speak. In some cases, they may even lead to more serious problems if left untreated. Whether you have healthy teeth or are battling the effects of cavities and decay, dental infections can affect anyone. They’re almost never pleasant, but with proper care and treatment, they can usually be managed quite easily. A dental infection is an outbreak of bacteria or other microorganisms in your mouth that begins in the gums or teeth and spreads over a period of time. Some dental infections are milder than others, but all can cause severe discomfort if not treated immediately. If you think you might have a toothache that’s not just from eating something too hot or cold, make an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible.
Dental infections originate at the tooth or its supporting structures and can spread to the surrounding tissue. These infections most commonly occur when bacteria invade the pulp and spread to surrounding tissues. Infections can also affect the gums causing gingivitis, which can later cause periodontal disease.
What causes dental infections?
Dental infections can happen to anyone, but they’re most often caused by bacteria in your mouth that travels to the gums and teeth. Bacteria is naturally occurring inside our mouths and stays on the surface of the teeth, gums, and tongue. When it gets in deep enough to form a small pocket (pus), it’s called an infection. Some of the most common types of bacteria that cause dental infections include:

There are also viruses that can cause dental infections, including herpes and Epstein-Barr. Bacteria can travel to your teeth any time you have an open cut inside the mouth, but it’s more likely to happen when gums are inflamed or have been pulled away from the teeth by receding gum tissue. There are many ways to get an infection in your mouth, and it can happen at any age.
Signs of a dental infection
Since every dental infection is unique and has its own set of symptoms, it can be tricky to spot one until it’s reached a serious phase. Most dental infections, though, have some similarities that are worth noting if you’re unsure what’s causing your discomfort.
Swelling in the Gums– One of the earliest signs of a dental infection is some swelling in the gums, as bacteria travels from the root of a tooth to the gum tissue surrounding it. The swelling may be mild or severe, and sometimes it covers the entire gum line.
Toothache- Another symptom of a tooth infection is pain that may or may not be described as a toothache. Toothaches can be sharp and sudden, or they can be more of a dull ache that never goes away.
Bad Breath– Bad breath can be caused by many things, but it’s often a sign of a dental infection. Bacteria in the mouth (and on the teeth) produces toxins that cause foul-smelling compounds. Mouth odors can be particularly strong if you have a gum infection.
Diagnosis of Dental Infection
- Tap on your teeth. A tooth that has an abscess at its root is generally sensitive to touch or pressure.
- Recommend an X-ray. Scan of the aching tooth can help identify an abscess. Your dentist may also use X-rays to determine whether the infection has spread, causing abscesses in other areas.
- Recommend a CBCT scan. If the infection has spread to other areas within your neck, a CBCT scan may be used to see how severe the infection is.

When to see a dentist instead of trying these techniques
Dental infections that aren’t treated right away can lead to more serious problems. Such as an abscess, tetanus, and loss of teeth. If you have the signs of a serious dental infection, you need to see a dentist instead of trying to treat it at home. In some cases, a mild toothache can be caused by a dental infection. But it doesn’t always progress to something more serious. A dentist can tell you if you have a dental infection and decide if you need antibiotics (or other treatment) to get rid of it.
Treatment incase of an infection
- Open and drain the abscess. The dentist makes a small cut into the abscess, allowing the pus to drain out. The dentist then washes the area with salt water (saline).
- Do a root canal. This can help get rid of the infection and save your tooth. To do this, your dentist drills down into your tooth, removes the diseased pulp and drains the abscess. The tooth may be capped with a crown to make it stronger, especially if this is a back tooth.
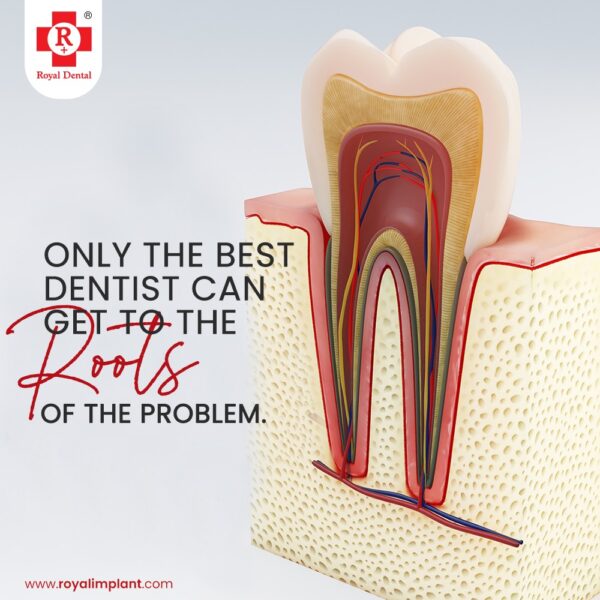
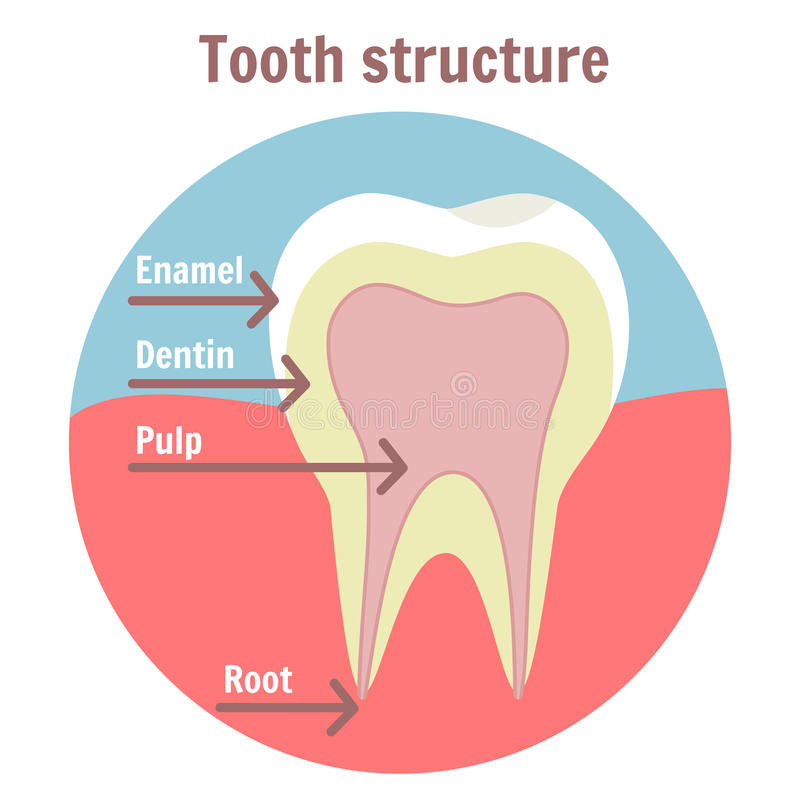
- Extract the affected tooth. If the affected tooth can’t be saved, your dentist will pull (extract) the tooth and drain the abscess to get rid of the infection.
- Prescribe antibiotics. If the infection is limited to the abscessed area, you may not need antibiotics. But if the infection has spread to nearby teeth, your jaw or other areas, your dentist will likely prescribe antibiotics to stop it from spreading further. Your dentist may also recommend antibiotics if you have a weakened immune system.
Seeing a dentist after trying these techniques
If you have a dental infection, you’ll likely be prescribed antibiotics. There are many different types of antibiotics, and some of them can be taken at home while others require you to go to the dentist’s office to take them. In some cases, antibiotics will clear up the infection on their own. While in others they might be paired with some other kind of treatment. To help prevent dental infections, you can visit the dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups. You can also help yourself by brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing once a day. Using mouthwash, and limiting sugary foods and drinks.
Conclusion
Dental infections can cause a lot of problems if they aren’t treated right away. So if you have any of the symptoms listed, see a dentist. Dental infections can be easily treated if caught in time, and most people can get antibiotic treatment at home. It’s important to brush and floss regularly, as well as use mouthwash, to help prevent dental infections from forming.