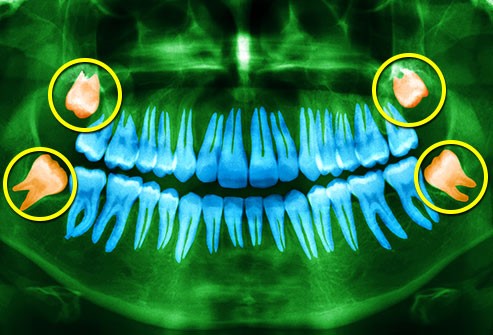
All that you must know about Wisdom Tooth | Royal Dental Clinics
Wisdom teeth are usually the last tooth to erupt. They are also called third molars. They are usually four in number in the oral cavity. Third molar teeth are the last posterior teeth to erupt. There are 4 wisdom teeth in the oral cavity: 2 each in the upper and lower jaws. They are placed at the end of the oral cavity. They erupt upto the age of 29 yrs. They can erupt fully like other teeth or can erupt partially or can be impacted in the bone.
A third molar tooth may need to be removed due to reduce mouth opening, pain or a higher chance for pathological changes. Wisdom tooth removal is a common procedure. An x-ray should be taken for diagnosis and treatment planning. The x-rays may point out the cause of pain which could be due to insufficient space for eruption, pressure on the adjacent tooth, cervical and root caries of the adjacent tooth, partially erupted third molar, decay of partially erupted wisdom teeth, limited mouth opening, cyst, abscess etc.
The above conditions can be treated with antibiotics, antiseptic mouthwashes, saltwater warm gargles and maintaining good oral hygiene. When the line of action does not suffice the surgical removal of wisdom tooth is considered. Also if there is no antagonist tooth against the wisdom tooth and if there is recurrent inflammation, one should consider removing a wisdom tooth.
Dr Chirag Chamria
Lip numbness is one of the possible complications of wisdom teeth removal. It happens when the nerve which lies in the vicinity to the wisdom tooth is damaged. It only causes sensation problems. It is usually temporary and may last from a few weeks to months. Sometimes the damage is permanent. The nerves running in close proximity to the wisdom tooth are inferior alveolar nerve, mental nerve branch of inferior alveolar nerve and lingual nerve. The incidence of inferior alveolar nerve damage while wisdom tooth removal is around 0.04 to 8 percent when the buccal approach is used.
The damage can cause prolonged anaesthesia or paresthesia causing impairment in speech, chewing, sleep and on patients overall mental state. When a split lingual bone technique we used chances of lingual nerve damage is more. Altered sensation in the tongue, chin and lower lip are most common symptoms. Painkillers and steroids are commonly prescribed medications in order to reduce the inflammation of the nerve. If the sensation doesn’t return back in 3 -4 months referral to a maxillofacial surgeon is needed.
Partially impacted:
Usually seen in lack of space in the upper and lower jaw, small jaw size. So there is not enough space for the wisdom teeth to erupt fully through the gums. It tries to erupt by applying pressure on front teeth so at times patient feels radiating pain in other teeth as well. While it tries to erupt it can cause a flap of tissue to remain over the tooth. This flap causes pain and swelling in the gingival tissue. This flap can trap food and bacteria resulting in gum and pain. This is termed as pericoronitis.
If the tooth is partially impacted it can develop a tissue over it which traps bacteria food debris resulting in pericoronitis. This causes pain, swelling, reduced mouth opening, hindrance in cleaning the area properly. Recurrent pain and swelling in such cases warrant removal of wisdom tooth. Partially impacted wisdom cause damage to neighbouring teeth and crowing. In such cases, the extraction of the wisdom tooth is considered.
Disimpacted wisdom tooth:
If the jaw size is small and if there is no space at all for the wisdom tooth to erupt then they get stuck or impacted in the jaw bone. It doesn’t necessarily cause pain.
So not in all situations wisdom teeth hurt. The dentist will suggest appropriate treatment if needed before any major symptoms develop.
When the third molar tooth is fully erupted but not in a straight line axis and is buccally placed it can result in cheek bite. Recurrent cheek bite and pain warrant its removal.
Impacted teeth become trapped within the jaw. These teeth can develop cyst that can damage the roots of other teeth and bone support. Such cases are also an indication of their removal. Extensive tooth decay of wisdom teeth also warrants wisdom tooth removal.
Wisdom tooth removal is a common surgical procedure performed in the oral cavity!
A radiological examination is of utmost importance in the extraction of wisdom tooth for determining its position, shape. Its tooth position can be fully submerged in the bone, partially submerged, mesioangular, distoangular, buccally placed, lingually placed, on the ascending ramus, depending upon shape it can have bulbous root, curved root, bifid root, conical root.
Once shape and position are determined it becomes easier to implement the best surgical extraction procedure. Also, inferior nerve anatomy and lingual nerve anatomy should be kept in mind to avoid damage to the nerve.
Position and shape of wisdom tooth determines the procedure:
- Wisdom tooth in a straight line axis or with conical root – This can be removed with a straight elevator and third molar forceps. The tooth is luxated in a figure of 8 motion for maxillary wisdom tooth and upward luxation for mandibular molars.
- Impacted wisdom tooth: An incision is made and the flap is reflected. The tooth is sectioned and bone guttering is carried out all around the submerged tooth. Elevators, root piece forceps, are used where ever required.
- Partially erupted wisdom tooth: An incision is made and the flap is reflected. Bone guttering is done. The tooth may or may not be sectioned. Elevators and forceps are used accordingly.
- Wisdom tooth removal should be removed with minimal trauma and damage to the adjacent tooth structures.




Leave a reply