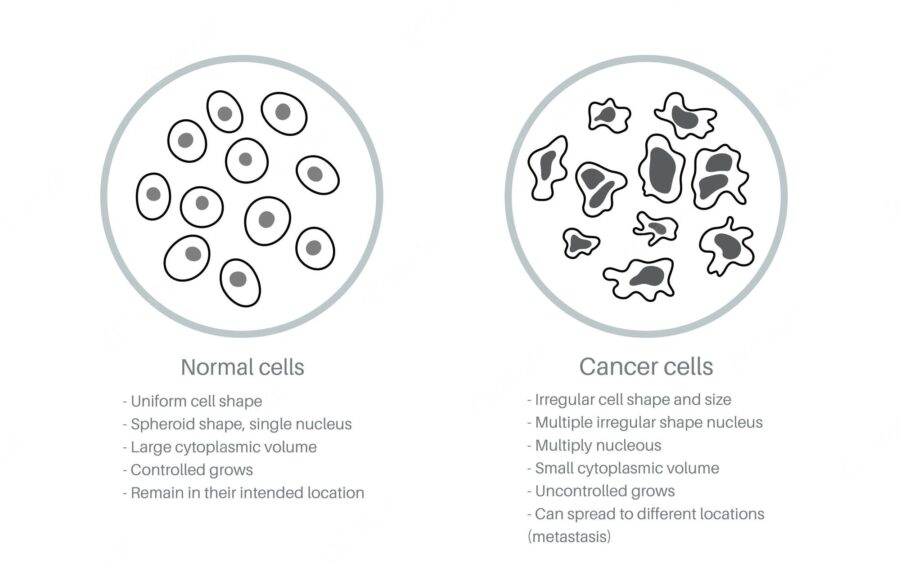
There are some fundamental differences between mouth ulcers (canker sores) and what may be cancer. Mouth ulcers are often painful whereas mouth cancer is not. Ulcers will clear up in about 2 weeks, whereas mouth cancer will not go away and will often spread. Mouth cancer patches may be rough, hard, and not easy to scrape off. Canker sores that are painful and do not heal within several weeks. So let us read more about whether it’s an ulcer or cancer.
What is an Ulcer?
Mouth ulcers are small white or red sores that form on your gums, lips, inner cheeks, or palate. They can be triggered by several different factors, including minor injuries, hormonal changes, and emotional stress. Mouth ulcers aren’t contagious — and they go away on their own — but there are treatments to help ease pain and discomfort. Most single mouth ulcers can try be avoided, such as: biting the inside of your cheek, badly fitting dentures, braces, rough fillings or a sharp tooth, and cuts or burns while eating or drinking – for example, hard food or hot drinks.
What are some ways to treat mouth ulcers?
- Use a rinse of saltwater and baking soda.
- Using SMYLE or DOLO-GEL cools the area.
- Covering mouth ulcers with baking soda paste.
- Applying ice to canker sores.

How long do mouth ulcers last?
Canker sores or ulcers are a common type of mouth ulcer that typically lasts 1–2 weeks. They usually occur for the first time during a person’s teenage years. People can treat canker sores with OTC pain-relieving gels, salt water rinses, and prescription medications.

Can I put salt on my ulcer?
Never put salt directly on an ulcer. Instead, you make a saltwater solution by mixing one teaspoon of salt in one cup of warm water. Swish it in your mouth or gargle it for about 30 seconds, then spit it out.
What is a Mouth cancer?
Mouth cancer refers to cancer that develops in any of the parts that make up the mouth (oral cavity). Mouth cancer can occur on the:
- Lips
- Gums
- Tongue
- The inner lining of the cheeks
- Roof of the mouth
- Floor of the mouth (under the tongue)
Cancer that occurs on the inside of the mouth is sometimes called oral cancer or oral cavity cancer. Mouth cancer is one of several types of cancers grouped in a category called head and neck cancers. Mouth cancer and other head and neck cancers are often treated similarly.
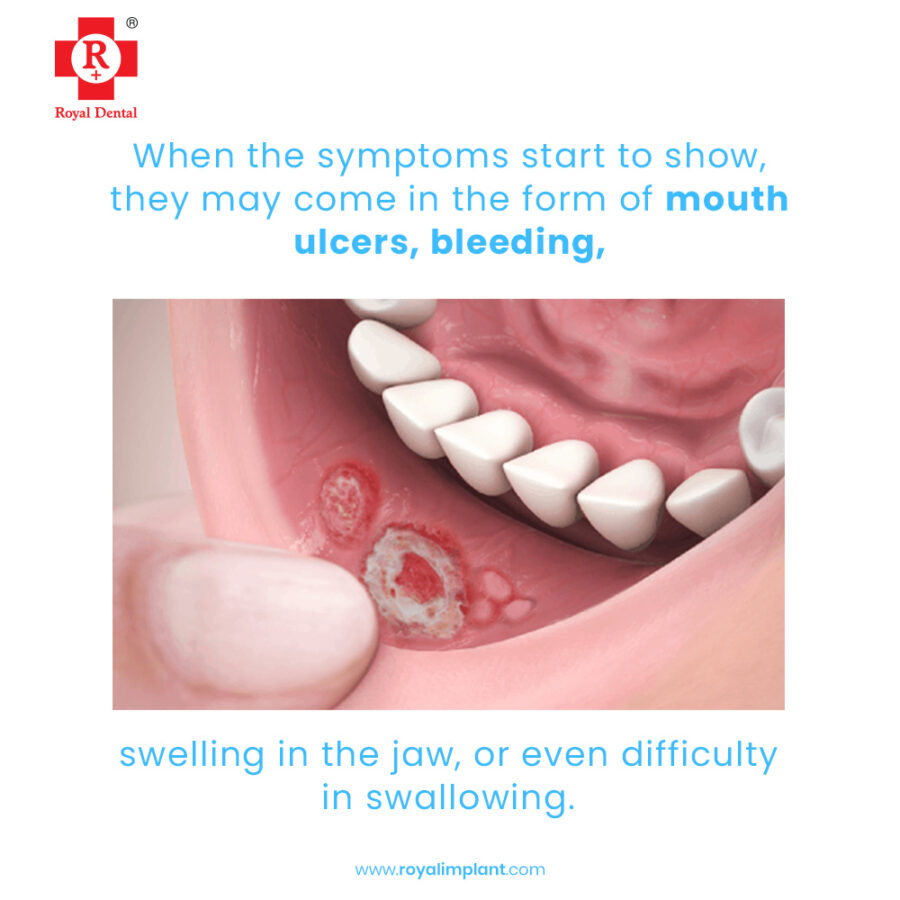
Signs and symptoms of mouth cancer may include:
- A lip or mouth sore that doesn’t heal.
- A white or reddish patch on the inside of your mouth.
- Loose teeth.
- A growth or lump inside your mouth.
- Mouth pain.
- Ear pain.
- Difficult or painful swallowing.
What do the Early stages of mouth cancer look like?
Sore in the mouth that doesn’t heal (the most common symptom). White or red patch on the gums, tongue, tonsils, or lining of the mouth. Loose teeth. The flat cells that cover the surfaces of your mouth, tongue, and lips are called squamous cells. The majority of mouth cancers begin in these cells. A patch on your tongue, gums, tonsils, or the lining of your mouth can signal trouble.
See a dentist!
Make an appointment with your doctor or dentist if you have any persistent signs and symptoms that bother you and last more than two weeks. Your doctor will likely investigate other more common causes for your signs and symptoms first, such as an infection.
ulcer vs cancer: Spot the difference between
- Mouth ulcers are often painful whereas mouth cancer is not.
- Cancer patches may be rough, hard, and not easy to scrape off.
- The majority of canker sores go away within 10 – 14 days.
- Oral cancer lesions don’t go away within that timeframe and persist indefinitely.
- Whereas a canker sore is usually painful, oral cancer may or may not cause pain.
Canker sores are always flat and usually have a white or yellow center (and turn gray as they’re healing). Oral cancer lesions can be flat or raised and are often white or red.
While canker sores can cause temporary, momentary pain when you have something acidic like orange juice, they don’t lead to chronic problems with swallowing, speaking, or chewing like oral cancer can.
Prevention of cancer
- Stop using tobacco or don’t start. If you use tobacco, stop. If you don’t use tobacco, don’t start. Using tobacco, whether smoked or chewed, exposes the cells in your mouth to dangerous cancer-causing chemicals.
- Drink alcohol only in moderation, if at all. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. For healthy adults, that means up to one drink a day for women of all ages and men older than age 65, and up to two drinks a day for men age 65 and younger.
- Avoid excessive sun exposure to your lips. Protect the skin on your lips from the sun by staying in the shade when possible. Wear a broad-brimmed hat that effectively shades your entire face, including your mouth. Apply a sunscreen lip product as part of your routine sun protection regimen.
- See your dentist regularly. As part of a routine dental exam, ask your dentist to inspect your entire mouth for abnormal areas that may indicate mouth cancer or precancerous changes.
Conclusion
Gastric ulcers and carcinomas are two different conditions that require two different treatments. An ulcer can be treated with lifestyle changes. If these don’t work, drugs can be prescribed. A carcinoma is treated with surgery. Drugs are often used as well.
Having an ulcer is not an indicator you will get cancer, nor does having cancer mean you are more likely to have another one in the future. An ulcer and carcinoma are both treatable conditions. To avoid these conditions, make sure you eat healthily and limit your stress.
© All rights reserved by Royal Dental Implants Pvt Ltd
Issued in public interest






