Toothache causes headache; has this ever crossed your mind and heart? A dental anatomy is important to understand. Then you are not by yourself. A toothache’s constant agony can actually cause a headache. Imagine yourself suffering from a painful toothache when, all of a sudden, you feel a pounding sensation in your head. Is this just a coincidence, or may there actually be a connection? Together, let’s solve the puzzle and investigate the possible causes of this double unease. We’ll avoid technical dentistry terms and intricate scientific concepts during our conversational adventure. Let’s investigate the fascinating issue, “Can toothache cause a headache?” while you take a seat.
Understand the Anatomy | Toothache and Headache
An understanding of anatomy is crucial to understanding the complex link between headaches and toothaches. Now let’s explore the two domains of dental and cerebral anatomy to understand the connectivity that is essential to this fascinating partnership.
Dental Anatomy
A tooth’s structure has several different components. The outermost layer, called enamel, serves as a barrier. The pulp contains blood vessels and nerves, whereas dentin rests below, supporting the pulp. It is easier to understand how toothaches can appear when any layer is weakened when this hierarchy is understood.
Nerves in the pulp convey sensory data, allowing humans to experience pressure and temperature sensations. A toothache may begin with increased sensitivity or excruciating pain when this delicate equilibrium is upset by conditions like decay or trauma.
Importance of Oral Health for Overall Well-Being:
Dental health is closely related to general health and is not separate from it. Due to the mouth’s role as a portal to the body, systemic disorders, including cardiovascular disease, have been connected to gum disease. Maintaining excellent dental health is crucial for one’s total physical well-being, as the holistic approach emphasizes.
The cornerstones of preventive measures include routine dental examinations, strict oral hygiene regimens, and early management of developing problems. Informing people about these procedures encourages a proactive attitude toward sustaining dental health and, hence, conserving general health.
Cranial Anatomy
The skull, which is made up of several bones serving different purposes, surrounds the brain like a fortress. Knowing this framework puts oral problems in context and helps explain how they can affect the complex balance in the cranial area. Adding the neck highlights the closeness of oral structures to important components of the cranial region. It emphasizes how problems with dental health may have an impact on the head and neck region as a whole.
Interconnection between Dental and Cranial Nerves:
The trigeminal nerve is an important component in this complex relationship. A key component of oral and cranial integration is this nerve, which sends sensory data from the face to the brain. Knowing that it is involved helps to explain how oral problems might cause headaches.
An illustration of the common routes connecting the cranial and oral nerves clarifies the possibility of a cascading effect. Disorders affecting the nerves in the mouth can interact with the nerves in the skull, opening a channel for pain impulses to pass through and perhaps causing headaches.
Explore Link Between Toothache and Headache
Shared Nerve Pathways
In-depth Analysis of the Trigeminal Nerve:
An extensive examination reveals the complex role that the trigeminal nerve, a major cranial nerve, plays in dental and cranial functions. The largest cranial nerve, it covers a vast portion of the face and oral cavity and splits into the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular divisions. This nerve is essential for oral connections and is responsible for delivering sensory impulses, including pain.
Knowing the structure and function of the trigeminal nerve reveals how oral cavity disruptions, like cavities or infections, can produce pain signals that travel along these branches, resulting in both localized toothaches and pain radiating into different areas of the head.
How Dental Pain Can Radiate to the Head
The intricate network of nerves that transmits sensory impulses in the face and mouth cavity, especially the trigeminal nerve, is the source of dental pain’s capacity to radiate to the brain. Pain signals from dental problems, such as cavities or infections, travel through the trigeminal nerve’s branches and into areas outside of the immediate oral cavity.
Dental discomfort can go all the way up to the forehead and temples since the trigeminal nerve covers a large area of the head. An overlap between a toothache and more generalised head pain is produced by the convergence of nerve pathways, which allows pain sensations to transition smoothly.
Headaches Associated with Toothaches
Tension Headaches and Their Correlation:
Increased muscle tension is commonly the cause of tension headaches, and this association is often observed in those who have bruxism (teeth grinding or clenching). Disorders of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which affect the jaw joint, can exacerbate tension headaches and cause muscle strain. There is a connection between oral health and the beginning of headaches: tension headaches can be caused by stretched facial muscles, especially those used for chewing.
Migraines and dental triggers:
Dental causes for migraines, which are notorious for their severe and incapacitating nature, are sometimes disregarded. Examine how certain stimuli, such as tooth pain—especially from untreated cavities or bruxism—can cause migraine attacks. People with migraines may be able to find relief by determining and treating the underlying dental reasons.
Dental Issues that Lead to Headaches
Tooth Decay
Insensitive pulp can be affected by tooth decay if it is not treated, in addition to the enamel and dentin. The trigeminal nerve pathways may be used by pain signals resulting from this invasion of the oral nerves to transmit headaches. A chain reaction of pain that may include headaches might result from the inflammatory reaction that decay causes in surrounding tissues. To appreciate the wider effects of untreated dental decay, one must comprehend this influence.
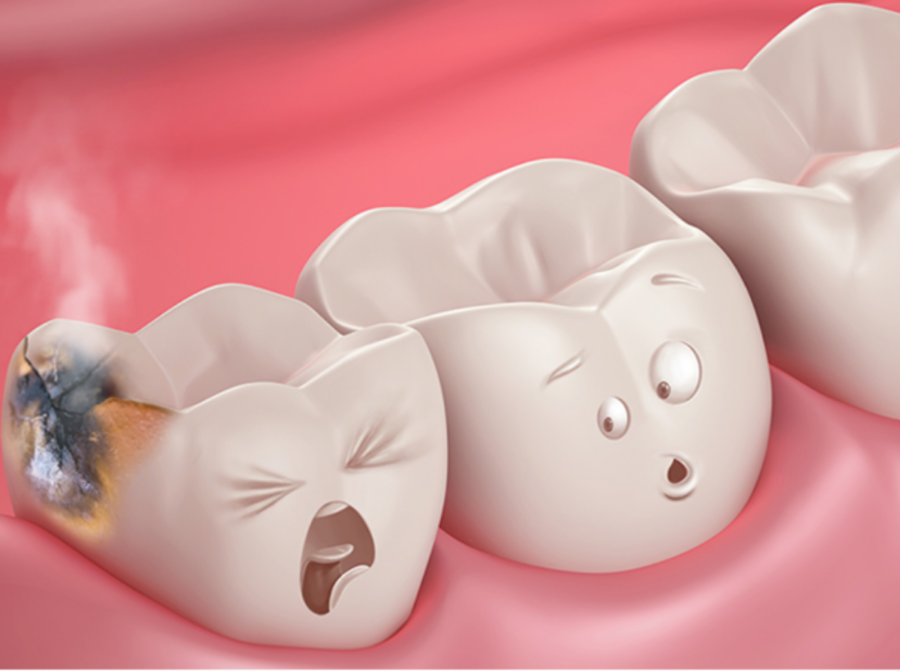

A comprehensive approach to dental treatment is essential, as evidenced by the identification of tooth decay as a possible cause of headaches. Toothaches can be properly treated, and related headaches can be effectively managed, by treating the underlying cause with procedures like fillings or root canals.
Gum Disease
Because gum disease is characterized by inflamed gums, headaches may be a result of the inflammatory reaction. The increased sensitivity of the nerves in the gums can send pain signals all the way up to the head, highlighting the connection between headaches and dental health.
Prolonged gum inflammation can have a long-lasting effect by serving as a constant headache trigger. Recognizing this link emphasizes how important it is to keep gum health at its best for general well-being. People with gum disease can reduce their chance of experiencing headaches from inflamed gums by treating the condition at an early stage.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
Disorders of the Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) affect how the jaw joint moves and how the muscles around it are used. Many symptoms, such as headaches, jaw pain, or difficulty eating, can result from this illness. Due to the TMJ’s close proximity to cranial tissues and its effect on the trigeminal nerve, pain can radiate into the brain. In order to relieve pain and avoid related headaches, effective care frequently entails individualized strategies, such as dietary changes, physical therapy, and dental procedures.
Home Remedies & Tip | Toothache and Headache
Immediate Relief Measures
Safe ways to alleviate toothaches and headaches temporarily:
- Cold Compress: Application to the affected area can help numb the pain.
- Saltwater Rinse: Gargling with warm salt water can reduce inflammation and provide relief.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Following recommended doses of pain relievers can temporarily alleviate discomfort.
- Clove Oil: Applying clove oil to the affected tooth can act as a natural analgesic.
When to seek professional help despite home remedies?
- Persistent Pain: If the toothache or headache persists despite home remedies, it’s crucial to consult a dentist.
- Signs of Infection: Swelling, pus, or fever may indicate an infection that requires immediate professional attention.
- Severe Pain or Discomfort: Intense, unbearable pain may signify a more significant dental issue that needs prompt intervention.
- Previous Dental Conditions: Individuals with a history of dental problems should seek professional help promptly to prevent escalation.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Daily habits to maintain optimal oral health:
- Regular Brushing: Emphasize the importance of brushing teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing: Incorporating daily flossing helps remove plaque and prevent gum disease.
- Mouthwash: Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can reduce bacteria and promote overall oral health.
- Tongue Cleaning: Cleaning the tongue helps eliminate bacteria that contribute to bad breath and oral issues.
- Proper Technique: Educate on the correct brushing and flossing techniques for effective plaque removal.
Impact on preventing toothache-related headaches:
- Reducing Inflammation: Proper oral hygiene minimizes gum inflammation, decreasing the likelihood of headache triggers.
- Preventing Tooth Decay: Regular brushing and flossing help prevent cavities, addressing a common cause of toothaches and headaches.
- TMJ Health: Good oral habits contribute to healthy temporomandibular joints, reducing the risk of headaches.
- Professional Cleanings: Regular dental check-ups and cleanings play a crucial role in preventing dental issues that may lead to headaches.
Conclusion
In summary, the complex relationship between headaches and toothaches—which are linked by similar nerve pathways—highlights the need for preventive dental care. Pain can be broken by treating conditions like gum disease, dental decay, and TMJ disorders. Preventive dental care is the key to a healthy smile free of headaches, according to Dr. Chirag Chamria. Your best defense against the query “Can Toothache Cause a Headache?” is routine examinations and careful dental hygiene. A better, pain-free tomorrow is guaranteed by proactive dental treatment today, which turns the obstacle into a route for long-term dental and general well-being.
All rights reserved by Royal Dental Implants Pvt Ltd., issued in public interest