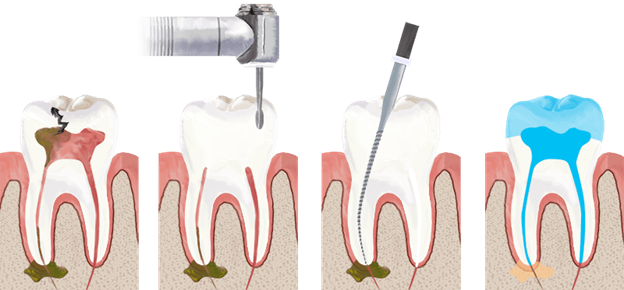
Oral health is important to general health, and we at Royal Dental Clinics couldn’t agree more. Gum disease, sometimes called periodontal disease, is a common but potentially significant dental ailment that may result in tooth loss, bone loss, and other issues. The signs of gum disease are often disregarded, which may lead to more serious oral health problems. Let us explore the dangers of ignoring gum disease or gingivitis and why it’s crucial to seek professional help for periodontitis. In this article, we’ll explore the dangers of ignoring gum disease symptoms and why it’s crucial to seek professional help as soon as possible.
Understanding Gum Disease
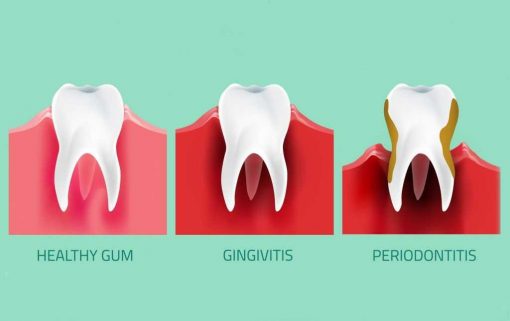
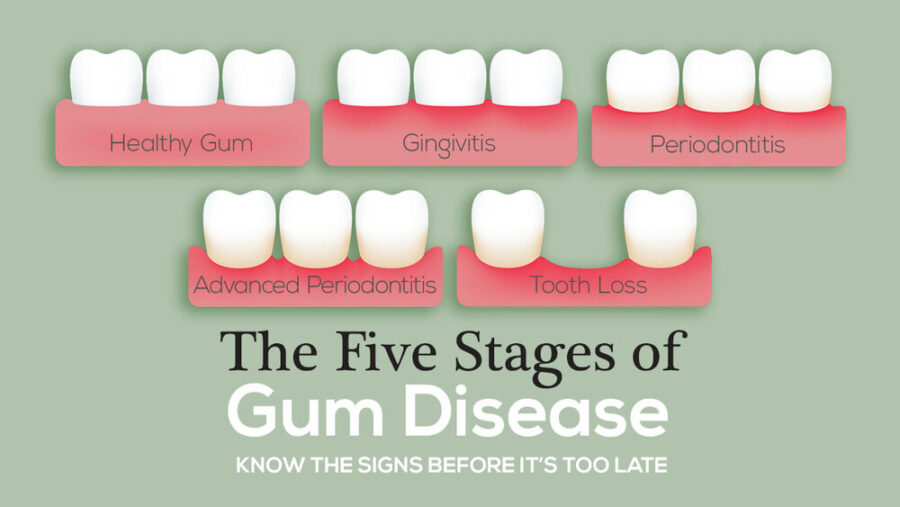
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It is a common condition that can range from mild inflammation to severe damage to the gums and bones that support the teeth. There are two types of gum disease:
- Gingivitis: This is the mildest form of gum disease and is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. Gingivitis is caused by a buildup of plaque, which is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth.
- Periodontitis: This is a more severe form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss. It occurs when the infection spreads below the gum line and starts to destroy the bone and tissues that support the teeth.
The primary cause of periodontal disease is poor oral hygiene. When plaque is not removed from the teeth through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. Other risk factors for gum disease include smoking, diabetes, hormonal changes, certain medications, and a family history of gum disease.
Treatment for gingivitis depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases of gingivitis, improved oral hygiene practices and professional cleanings can help reverse the condition. More advanced cases of gum disease may require scaling and root planing, gum surgery, or even tooth extraction in severe cases. Preventing gum disease is key to maintaining good oral health. This includes practicing good oral hygiene, eating a healthy diet, and visiting the dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups.
Symptoms of Gum Disease or Gingivitis
The early symptoms of gum disease are often mild and can be easy to ignore. However, if left untreated, these symptoms can progress and become more severe. The common symptoms of gum disease include:
✤ Bleeding gums when brushing or flossing
✹ Red, swollen, or tender gums
✤ Receding gums
✹ Bad breath
✤ Loose or shifting teeth
✹ Pus between the teeth and gums
✤ Changes in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
Causes of Gum Disease or Gingivitis
It is caused by the bacteria in dental plaque, which is a sticky film that forms on teeth and gums. However, there are several other factors that can increase the risk of developing gingivitis.
Poor oral hygiene: Neglecting proper oral hygiene habits, such as not brushing and flossing regularly, can lead to a buildup of plaque on teeth and gums, causing gum disease.
Smoking and tobacco use: Tobacco use can affect the health of the gums and increase the risk of developing gum disease. It can also make treatment less effective.
Genetics: Some people are more susceptible to gum disease due to genetic factors that affect the immune system’s response to bacteria.
Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to gum disease.
Certain medications: Some medications, such as antihistamines, antidepressants, and blood pressure medications, can reduce saliva flow, making it easier for bacteria to thrive in the mouth and cause gum disease.
Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, HIV, and cancer, can increase the risk of developing gum disease.
Poor nutrition: A diet lacking in essential nutrients can weaken the immune system and make it more difficult to fight off gum disease.
To Know More on periodontal disease Read On here.
Risks of ignoring Gum Disease symptoms
Ignoring the symptoms of gum disease can have serious consequences on your oral health. Here are some risks associated with ignoring gingival issues symptoms:
Tooth loss: Gum disease can cause damage to the bone and tissues that support the teeth, leading to tooth loss. This can significantly impact your ability to eat, speak, and smile confidently.
Gum recession: They can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets where bacteria can thrive. Over time, this can lead to gum recession, exposing the roots of the teeth and causing sensitivity.

Chronic bad breath: The bacteria that cause gum disease can also cause chronic bad breath or halitosis, which can be embarrassing and difficult to manage.
Systemic health problems: Research has shown a link between gum disease and systemic health problems such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and respiratory infections. Ignoring gum disease symptoms can increase the risk of developing these health problems.
Expensive treatments: Treating advanced gum disease can be costly and time-consuming. If left untreated, gum disease can require more invasive and expensive treatments such as periodontal surgery or tooth replacement.
How Gum Disease can affect your overall health?
Cardiovascular disease: Studies have shown a link between gingivitis and an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. The bacteria that cause gum disease can enter the bloodstream and contribute to the formation of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Diabetes: They can make it harder to control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. The inflammation caused by gum disease can also make diabetes symptoms worse.
Respiratory infections: The bacteria that cause gum disease can travel from the mouth to the lungs and cause respiratory infections such as pneumonia and bronchitis.
Pregnancy complications: Pregnant women with gum disease are at a higher risk of preterm birth and low birth weight babies.
Alzheimer’s disease: Some studies have suggested a link between gum disease and an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Rheumatoid arthritis: Studies have shown a connection between gum disease and an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis, possibly due to the inflammation caused by gum disease.
Prevention Tips agter Gum Treatment
Brush twice a day: Brush your teeth for at least two minutes twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste. Be sure to brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the gumline.
Floss daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between teeth and along the gumline. Be gentle and avoid snapping the floss against your gums.
Use mouthwash: Antimicrobial mouthwash can help kill bacteria that cause gum disease. Use it after brushing and flossing.
Quit smoking: Smoking increases the risk of gum disease and makes it harder to treat. Quitting smoking can help improve oral health and overall health.
Eat a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help prevent gum disease by providing essential nutrients for gum health.
Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental cleanings and checkups can help detect and prevent gum disease. Your dentist can also provide personalized recommendations for maintaining good oral hygiene.
Manage stress: Stress can weaken the immune system and make it harder to fight gum disease. Practice stress-reducing activities such as meditation, exercise, or hobbies.
By following these gingivitis prevention tips, you can help maintain good oral and overall health. If you experience any symptoms of gum disease, such as bleeding gums or bad breath, seek professional dental care as soon as possible. Early detection and treatment can help prevent the progression of gum disease and reduce the risk of complications.
Treating Gum – Periodontal Disease
If you have been diagnosed with gum disease, it’s important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent further damage to your teeth and gums. Here are some common treatments for gum disease offered at Royal Dental Clinics by Dr. Chirag Chamria:
Scaling and root planning: This is a deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar from the teeth and root surfaces. It helps to remove bacteria and toxins that cause gum disease.
Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat gum disease if scaling and root planning alone are not enough. Antibiotics can be taken orally or applied directly to the affected areas.
Laser therapy: Laser therapy is a non-surgical treatment that uses a dental laser to remove diseased tissue and promote healing.
Gum surgery: In more severe cases of gum disease, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue and reshape the gums. This can help to reduce pocket depth and improve the overall health of the gums.
Bone grafting: If the bone supporting your teeth has been damaged by gum disease, bone grafting may be necessary to rebuild the bone and prevent tooth loss.
Dental implants: If you have lost teeth due to gingival disease, dental implants may be an option to replace them. Implants are surgically placed in the jawbone and can help to prevent further bone loss and improve overall oral health.
Importance of regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are essential for maintaining good oral health and preventing gingivitis disease. Here’s why they are important, according to Dr. Chirag Chamria:
Early detection: During a dental check-up, your dentist will examine your teeth and gums for signs of gum disease. Catching gum disease in its early stages makes it easier to treat and can prevent further damage to your teeth and gums.
Professional cleaning: Regular dental cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup that can lead to gingival disease. Even with good oral hygiene habits at home, it’s difficult to remove all plaque and tartar without professional cleaning.
Personalized recommendations: Your dentist can provide personalized recommendations for maintaining good oral hygiene and preventing gingival disease. They may recommend specific products or techniques to help keep your teeth and gums healthy.
Overall health assessment: Your dentist can also assess your overall health during a dental check-up. Some health conditions, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of this disease. Your dentist may refer you to a healthcare provider for further evaluation and management.
Preventing complications: Untreated gum disease can lead to complications such as tooth loss and bone damage. Regular dental check-ups and proper treatment can help prevent these complications.
Conclusion
Patients with dental problems, such as gum disease, are urged to see Royal Dental Clinics as soon as they notice any symptoms. Ignoring the signs of gum disease may lead to more serious oral health problems, so it’s important to take preventative measures and talk to your dentist about any concerns you have. Gum disease and other dental disorders may be prevented with regular dental examinations, proper oral hygiene practices, and early intervention, resulting in a beautiful smile for life.
Suggested Article:
Types of Periodontal Disease and Cure
Follow Us For More Updates