Gum disease, also known as periodontal, affects many people and can have a range of causes and effects. It can range from mild gum inflammation to severe damage to the bone and tissues that support the teeth. Different types of gum disease exist, each requiring its own approach to prevention and treatment. For example, gingivitis is the mildest form of gum disease, and it can usually be reversed with proper brushing and flossing. Aggressive periodontitis is more severe and can cause deep pockets between the teeth and gums, resulting in tooth loss. As gum disease progresses, it is important to pay attention to the signs and symptoms and seek treatment as soon as possible.
What is Gum Disease?
Gingival disease, also known as periodontal, is an infection of the tissues that support your teeth and can be caused by a number of factors. It is an inflammatory condition that affects the gums and can lead to bone and tooth loss if left untreated. When the gums are healthy, they form a tight seal around the teeth, preventing bacteria and plaque from building up and causing infection. However, when the gums become inflamed, they become prone to infection, and the bacteria and plaque can build up, leading to gingival infection.

There are two main stages of this disease: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the mildest form of and is reversible with proper brushing and flossing. If left untreated, however, it can progress to periodontitis, the more severe form of gum disease. Periodontitis can cause deep pockets to form between the teeth and gums, and can eventually lead to tooth loss.
Symptoms of gum disease can include red, swollen, or tender gums, gums that bleed easily, bad breath, receding gums, and loose teeth. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible, as gum disease can be treated if caught early.
Types of Gum Disease
Gingivitis Gum Disease
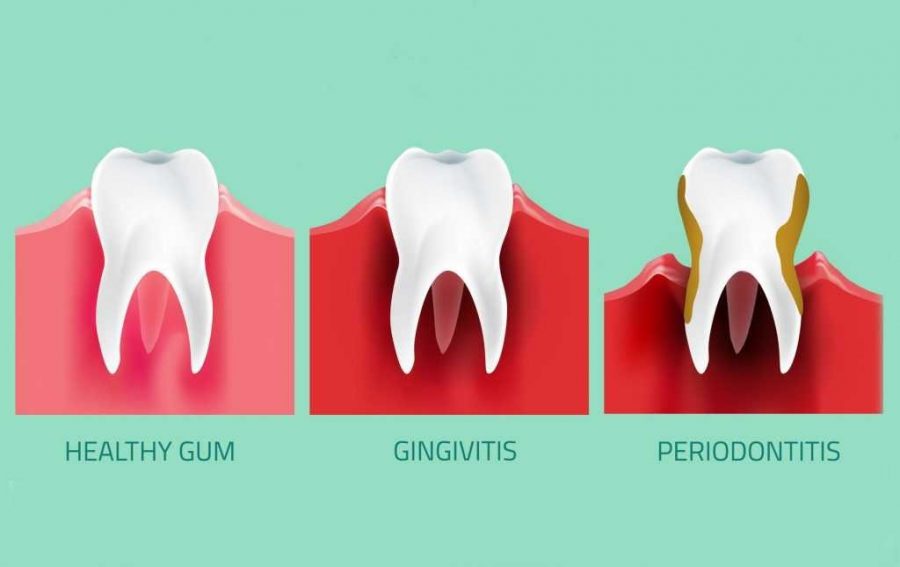
Gingivitis is the mildest form of gum disease and is characterised by inflammation of the gingiva. It is usually caused by poor oral hygiene, such as not brushing and flossing regularly or not brushing properly. The symptoms of gingivitis include red, swollen, and tender gums; bleeding gums; and bad breath. Fortunately, gingivitis can usually be reversed with proper brushing and flossing, as well as regular visits to the dentist.
Gingivitis is the milder form of gum disease and is caused by the buildup of plaque on the teeth and gums. The symptoms of gingivitis include red, swollen, and bleeding gums, and can often be reversed with improved oral hygiene practices such as regular brushing and flossing, and professional dental cleanings.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is more severe than gingivitis and is characterized by deep pockets between the teeth and gums. These pockets can become infected and cause the gums, teeth, and bones to deteriorate. If left untreated, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss. The symptoms of periodontitis include receding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth.
Periodontitis is a more severe form of gum disease that occurs when the inflammation and infection spreads to the deeper tissues and bones that support the teeth. Symptoms of periodontitis include gum recession, loose teeth, and even tooth loss. Treatment for periodontitis usually involves scaling and root planing (a deep cleaning procedure), antibiotics, and, in more severe cases, surgery.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
The most common symptom of gum disease is bleeding gingiva. This can happen when brushing and flossing and can be a sign that the gums are inflamed and infected. Other symptoms of gum disease include red, swollen, or tender gingiva, receding gingiva, bad breath, and loose teeth. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
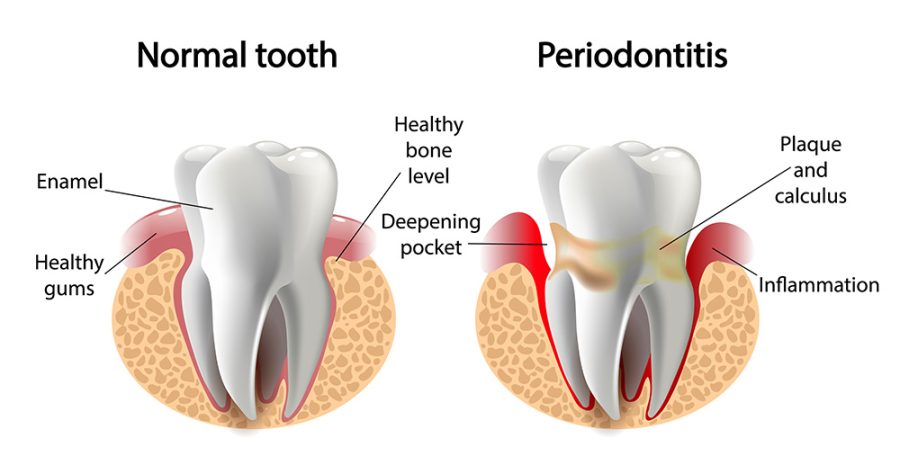
Causes of Gum Disease
Gum disease can be caused by a number of factors, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, certain medications, genetics, and certain medical conditions. Poor oral hygiene is the most common cause of gingival disease, as it allows bacteria and plaque to build up, leading to infection. Smoking can also contribute to gum disease, as it can reduce the body’s ability to fight infection and can increase the risk of gum infection. Additionally, certain medications and medical conditions, such as diabetes, can also increase.
Prevention of Gum Disease
The best way to prevent gingival disease is to practice good oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and seeing your dentist regularly for professional cleanings. Additionally, quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and managing any medical conditions that may increase the risk of gum infection can also help to prevent it.
Treatment of Gum Disease
The treatment depends on the severity of the condition. For mild cases of gingivitis, a combination of proper brushing and flossing,as well as regular dental cleanings, may be enough to reverse the condition. For more advanced cases of periodontitis, however, more aggressive treatment may be necessary. This may include scaling and root planing, antibiotics, or even surgery. It is important to seek treatment as soon as possible, as gum infection can progress quickly and can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
In terms of cure, the best approach is prevention. Practicing good oral hygiene habits such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and regular visits to the dentist for cleanings and check-ups can help prevent gingival disease from developing in the first place. If gum disease has already developed, seeking prompt treatment from a dental professional is essential to prevent further damage and potential tooth loss. In addition to professional treatment, maintaining good oral hygiene practices at home can help manage and prevent the progression of gum infection.
Importance of Good Oral Hygiene | Gum Disease
Good oral hygiene is essential for maintaining healthy teeth and gums. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and seeing your dentist regularly for professional cleanings. Additionally, it is important to use an antibacterial mouthwash to help reduce bacteria in the mouth. By practicing good oral hygiene, you can help to prevent gum disease and maintain a healthy mouth and smile.
When to See a Dentist?
If you notice any symptoms of gum disease, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible. A dentist can evaluate your condition and determine the best course of treatment. Additionally, it is important to see a dentist for regular cleanings and checkups. As this can help to prevent gum disease and maintain a healthy mouth and smile.
Conclusion
Gingival disease is an infection of the tissues that support your teeth. And can be caused by poor oral hygiene, smoking, certain medications, and medical conditions. There are two main stages: gingivitis and periodontitis. Symptoms of gum infection include bleeding gums, red or swollen gums, receding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth. Treatment of gum disease varies depending on the severity but may include a combination of scaling and root planing, antibiotics, and surgery. The best way to prevent gum disease is to practice good oral hygiene. Such as brushing and flossing regularly and seeing your dentist for regular checkups and professional cleanings.