One issue that may be keeping you up at night is bruxism in children, which is just another word for teeth grinding. It’s more prevalent than you would believe, and the key to assisting your child in navigating this dental difficulty is knowing the indications, causes, and remedies. Imagine the gentle hum of your child’s dream world broken up by teeth-gnashing. Unsettling, huh? This blog will help us solve the puzzle of paediatric bruxism by examining the often-overlooked minor signs, possible causes of this nighttime symphony, and—above all—managing techniques to calm those little teeth. Together, we will explore the realm of bruxism and acquire the necessary information to preserve those priceless smiles. All set? Come on, let’s go!
What is Bruxism?
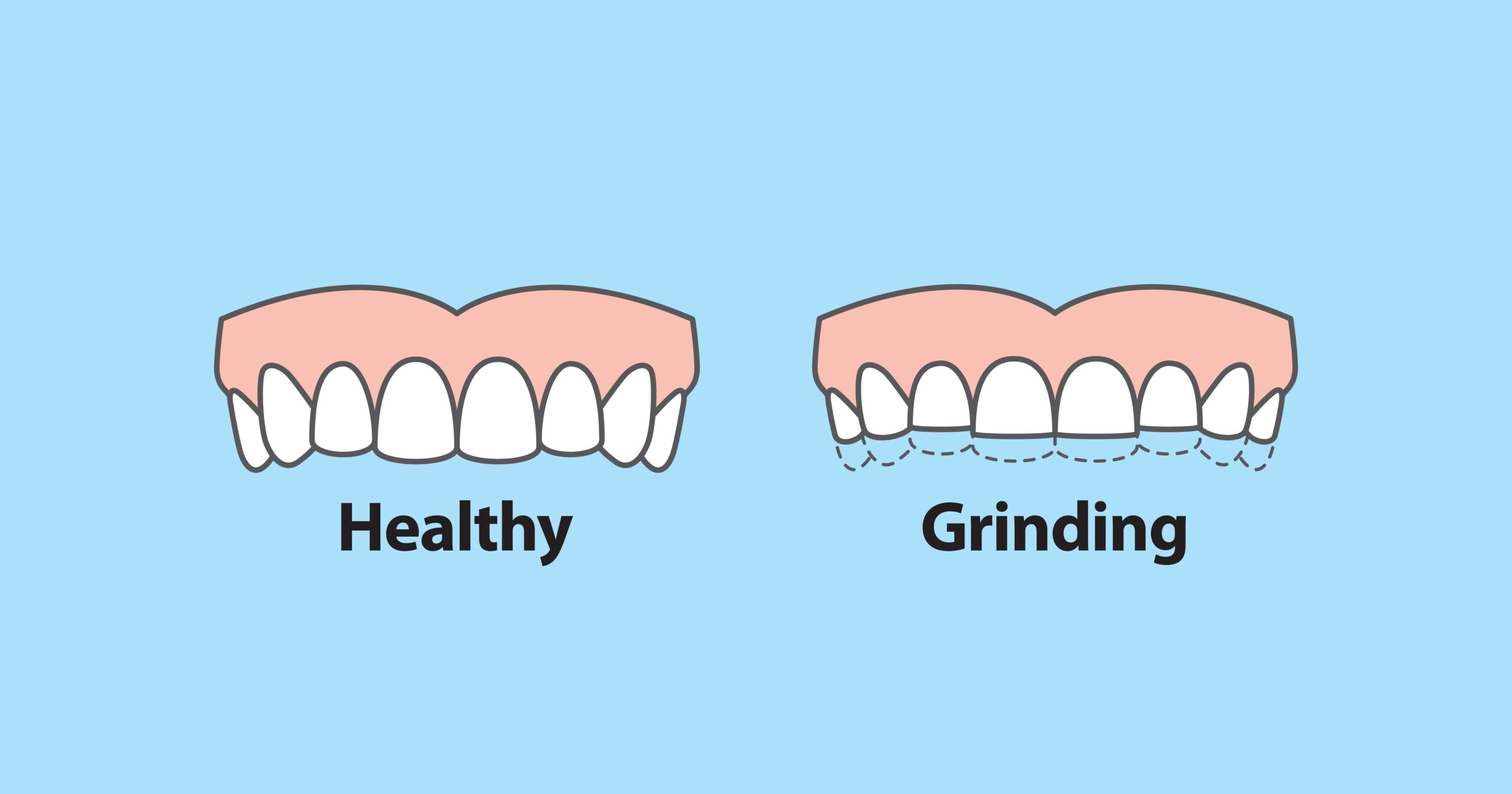
The term “bruxism,” which may sound foreign to you, describes the behavior of clenching or grinding one’s teeth, and it is not limited to adults. Bruxism in children is quite a common, although sometimes misinterpreted, condition. In essence, it is a recurrent, involuntary movement of the jaw that causes teeth to grind together. This can happen during the day or, more frequently, when you’re sleeping at night. Early diagnosis and prevention of possible dental issues are contingent upon the identification of bruxism in youngsters.
Signs of bruxism in children might include damaged tooth surfaces, heightened sensitivity to light, jaw pain, headaches (particularly in the morning), and irregular sleep patterns. Recognizing and treating bruxism in its early phases begins with an understanding of these characteristics.
Primary vs. Secondary Bruxism
To comprehend bruxism fully, it’s essential to distinguish between primary and secondary forms of the condition.
Primary Bruxism: This type of bruxism is not associated with any other medical or dental condition. It is often considered a habitual behavior and is more prevalent in children. The exact cause of primary bruxism is not always clear, but factors such as stress, anxiety, or teeth misalignment may contribute.
Secondary Bruxism: Unlike primary bruxism, secondary bruxism is linked to an underlying medical or dental issue. It can be a symptom of conditions like sleep disorders, respiratory problems, or neurological disorders. Identifying and treating the root cause of secondary bruxism is crucial for effective management.
Common Misconceptions Debunked
Myth: Bruxism is a Habit That Will Naturally Go Away: While some children may outgrow bruxism, it’s not a certainty. Addressing the underlying causes and implementing preventive measures is essential to ensuring optimal oral health.
Myth: Bruxism Only Affects Permanent Teeth Both primary and permanent teeth can be affected by bruxism. Early detection and intervention are vital to prevent potential damage to developing teeth.
Myth: Bruxism is Harmless in Children: Bruxism can lead to various dental issues, including tooth wear, sensitivity, and jaw pain. Ignoring these symptoms may result in more severe complications over time.
Signs and Symptoms
Teeth Grinding and Clenching:
- One of the primary signs of bruxism is the audible grinding or clenching of teeth, often noticed during sleep.
- Children may grind their teeth during the day as well, especially when under stress or concentrating.
Jaw pain and fatigue:
- Bruxism can lead to jaw discomfort and fatigue due to the repetitive motion of grinding or clenching.
- Children may complain of soreness in the jaw muscles, particularly in the morning.
Headaches and earaches:
- Persistent headaches, especially in the morning, can be indicative of bruxism.
- Earaches without an apparent infection may also be linked to the muscular strain caused by tooth grinding.
Impact on Oral Health
Beyond the observable signs, bruxism can have a significant impact on a child’s oral health. Understanding these consequences is vital for informed decision-making and proactive dental care.
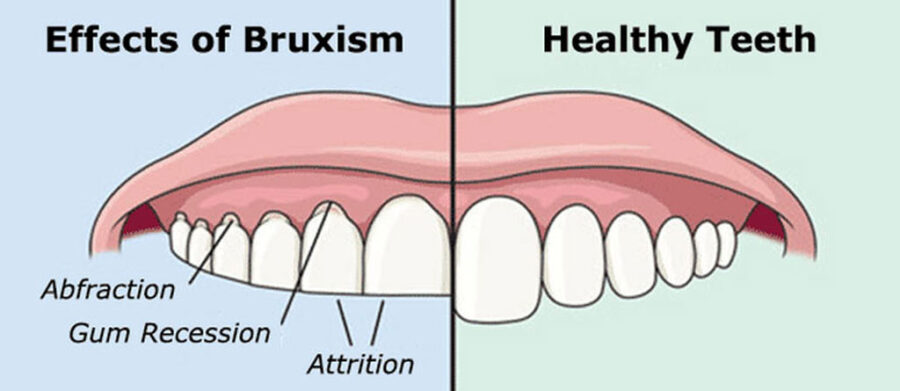
Dental wear and tear:
- The constant grinding of teeth can result in accelerated wear and tear on the tooth surfaces.
- Over time, this can lead to flattened, chipped, or sensitive teeth, affecting the overall integrity of the dentition.

Enamel Damage:
- Bruxism poses a risk to the enamel, the protective outer layer of the teeth.
- Enamel erosion may occur, making teeth more susceptible to cavities and other dental issues.
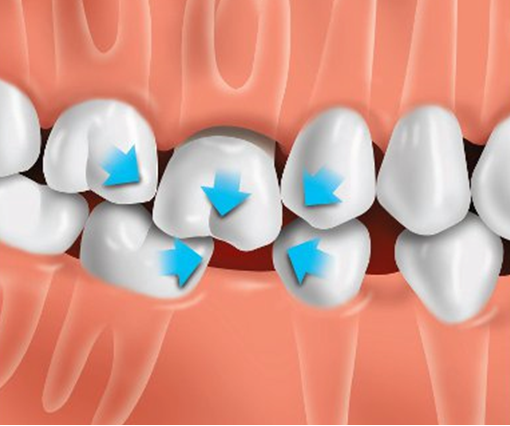
Alignment Issues:
- Prolonged bruxism can contribute to misalignment issues in both primary and permanent teeth.
- The uneven forces exerted during grinding may affect the natural positioning of teeth, potentially requiring orthodontic intervention.
Causes of Bruxism in Children
Understanding the underlying causes of bruxism in children is essential for effective management. The triggers can be multifaceted, encompassing both psychological and physiological factors. Let’s delve into the intricate web of influences that contribute to bruxism:
Psychological Factors
Stress and anxiety:
Children, like adults, can experience stress and anxiety, whether related to school, family dynamics, or other factors. Dr. Chirag Chamria notes that heightened stress levels may manifest as bruxism in children, making stress management an integral part of addressing the root cause.
Emotional Upheaval:
Major life changes, emotional upheaval, or challenging experiences can contribute to bruxism. Children may lack the verbal skills to express their emotions, leading to the expression of distress through teeth grinding.
Sleep Disorders:
Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or night terrors, can disrupt the sleep cycle and contribute to bruxism. Identifying and addressing these underlying sleep issues is crucial for comprehensive bruxism management.
Physiological Factors
Malocclusion:
Malocclusion, or misalignment of teeth, is a common physiological factor associated with bruxism. Dr. Chamria emphasizes the importance of early orthodontic assessments to identify and address malocclusion, preventing its potential contribution to bruxism.
Airway Issues:
Breathing difficulties, such as issues with the airway, can influence bruxism in children. Addressing respiratory concerns, such as allergies or enlarged tonsils, may alleviate the physiological triggers of tooth grinding.
Neurological Factors:
Certain neurological factors can contribute to bruxism, including hyperactivity or conditions like cerebral palsy. Dr. Chirag Chamria highlights the need for a thorough assessment by a healthcare professional to identify and manage neurological factors associated with bruxism.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Ensuring an accurate diagnosis of bruxism in children is pivotal for effective management and prevention of potential complications. Dr. Chirag Chamria sheds light on the comprehensive process of diagnosis and evaluation:
The importance of Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups play a crucial role in the early detection of bruxism in children. Dr. Chamria underscores the significance of routine visits to the dentist for monitoring oral health and identifying signs of tooth grinding. These check-ups provide an opportunity for proactive intervention, helping to address bruxism before it leads to more significant dental issues.
Dental History and Patient Interviews
Understanding a child’s dental history and conducting patient interviews are integral components of the diagnostic process. Dr. Chamria explains that gathering information about the child’s oral hygiene practices, previous dental treatments, and any reported symptoms of bruxism is essential. Patient interviews, especially with parents and caregivers, can reveal behavioral patterns, stressors, or lifestyle factors that may contribute to the condition.
Utilising Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Digital Impressions:
Digital impressions provide a detailed and accurate three-dimensional representation of the teeth. Dr. Chamria explains that these impressions aid in assessing the extent of dental wear and identifying any abnormalities in tooth surfaces caused by bruxism.
X-rays and imaging:
X-rays and imaging techniques are essential for evaluating the structural aspects of the teeth and jaw. Dr. Chamria emphasizes the role of X-rays in detecting any underlying issues, such as malocclusion or abnormalities in tooth structure, contributing to bruxism.
Monitoring sleep patterns:
Understanding a child’s sleep patterns is crucial, as bruxism often occurs during sleep. Dr. Chamria advocates for tools that monitor sleep patterns, such as sleep studies, to identify any disruptions that may be associated with teeth grinding.
Effects of Untreated Bruxism
Understanding the potential consequences of untreated bruxism in children is paramount for parents and caregivers. Dr. Chirag Chamria sheds light on the long-term dental complications, overall health impact, and crucial role of early intervention:
Dental wear and damage:
Untreated bruxism can lead to extensive dental wear, affecting the enamel and overall tooth structure. Dr. Chamria emphasises that over time, this wear can result in flattened, chipped, or sensitive teeth, compromising their function and aesthetics.
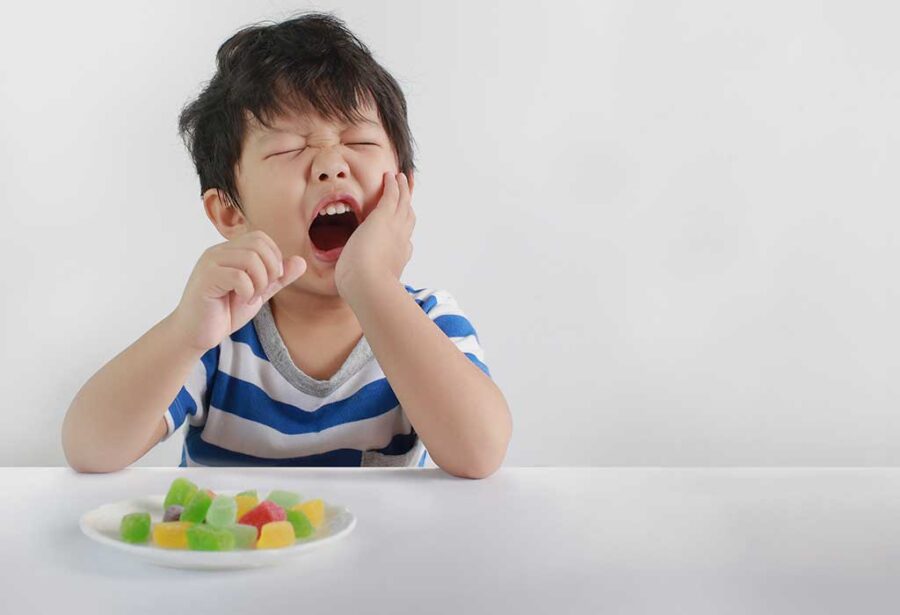

Misalignment Issues:
Prolonged tooth grinding can contribute to misalignment issues in both primary and permanent teeth. Dr. Chamria notes that addressing misalignment early is vital to prevent more complex orthodontic issues later in a child’s development.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders:
The constant strain on the jaw muscles during bruxism may lead to TMJ disorders. Dr. Chamria highlights that untreated bruxism can contribute to jaw pain, difficulty in opening and closing the mouth, and other TMJ-related complications.
Impact on Overall Health
Sleep Disturbances:
Bruxism often occurs during sleep, contributing to disruptions in sleep patterns. Dr. Chamria explains that inadequate sleep can have cascading effects on a child’s overall health, affecting mood, cognitive function, and general well-being.
Chronic pain and discomfort:
Persistent jaw pain, headaches, and earaches resulting from untreated bruxism can lead to chronic discomfort. Dr. Chamria underscores the importance of addressing these symptoms to improve a child’s overall quality of life.
The Role of Early Intervention
Early intervention is a key component in mitigating the long-term effects of bruxism in children. Dr. Chamria emphasizes the following:
Customized Treatment Plans:
Tailored treatment plans, including dental appliances, orthodontic interventions, and stress management strategies, can effectively address bruxism. Dr. Chamria advocates for early identification and personalized approaches to prevent the progression of dental complications.
Parental Awareness and Collaboration:
Educating parents and caregivers about the signs of bruxism and the importance of early intervention is crucial. Dr. Chamria stresses the role of collaborative efforts between dental professionals and parents in monitoring and addressing bruxism in children.
Dr. Chirag Chamria’s Treatment Approach
Customised Night Guards and Appliances
Dr. Chamria advocates for the use of customised night guards and dental appliances for children with bruxism. These devices are meticulously designed to fit a child’s mouth, providing a protective barrier that minimizes the impact of teeth grinding and clenching during sleep.
Effectiveness in Children:
Customized night guards are highly effective in preventing dental wear and reducing the strain on jaw muscles. Dr. Chamria notes that early implementation of these appliances can significantly contribute to the prevention of long-term complications associated with bruxism in children.
Behavioral Interventions
Stress Management Techniques:
Addressing the psychological aspects of bruxism, Dr. Chamria recommends stress management techniques tailored for children. These may include age-appropriate mindfulness practices, expressive activities, or positive reinforcement strategies to alleviate stressors that contribute to teeth grinding.
Relaxation Exercises:
Incorporating relaxation exercises into a child’s routine can be beneficial for reducing tension and promoting overall well-being. Dr. Chamria emphasizes the importance of teaching children relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or guided imagery, to manage stress and mitigate the occurrence of bruxism.
Collaboration with Pediatric Specialists
Orthodontists:
Dr. Chamria highlights the role of orthodontists in addressing malocclusion and misalignment, common contributors to bruxism. Collaborative efforts between dentists and orthodontists ensure a comprehensive approach to correcting structural issues that may exacerbate tooth grinding.
Sleep Medicine Experts:
Collaboration with sleep medicine experts is essential in cases where bruxism is associated with sleep disorders. Dr. Chamria stresses the importance of a multidisciplinary approach, where sleep specialists can contribute to the diagnosis and management of sleep-related aspects of bruxism.
Psychologists:
In cases where emotional factors contribute to bruxism, collaboration with psychologists can be invaluable. Dr. Chamria encourages a holistic approach that addresses the psychological well-being of the child, ensuring that emotional factors are appropriately managed.
Conclusion
To sum up, parents and other caregivers need to understand bruxism in children. Key insights are highlighted by Dr. Chirag Chamria, who emphasizes the need of early symptom recognition. Accurate diagnosis is aided by comprehensive care, modern diagnostic equipment, and dental examinations. Untreated bruxism can have an adverse effect on general health and cause dental problems. In order to reduce long-term impacts, prompt action is essential, including individualized treatment regimens. In order to provide our children with the best possible oral health, Dr. Chamria promotes obtaining expert advice and working in tandem with dental specialists. To guarantee a healthier and more radiant smile tomorrow, always remember to take preventative measures today.