At times even if you have no cavity, yet have severe tooth pain when you bite on food? The cause could be a cracked tooth. If you have throbbing, constant pain, you may have an infected tooth. You should see your dentist about this issue as soon as possible. This abscess in tooth, has possibility of spreading to your mouth or neck. From a cavity to infected gums, a tooth can have a lot of causes. Whether your toothache feels dull and achy or sharp and throbbing, there is a solution. Read more on hyperaemia.
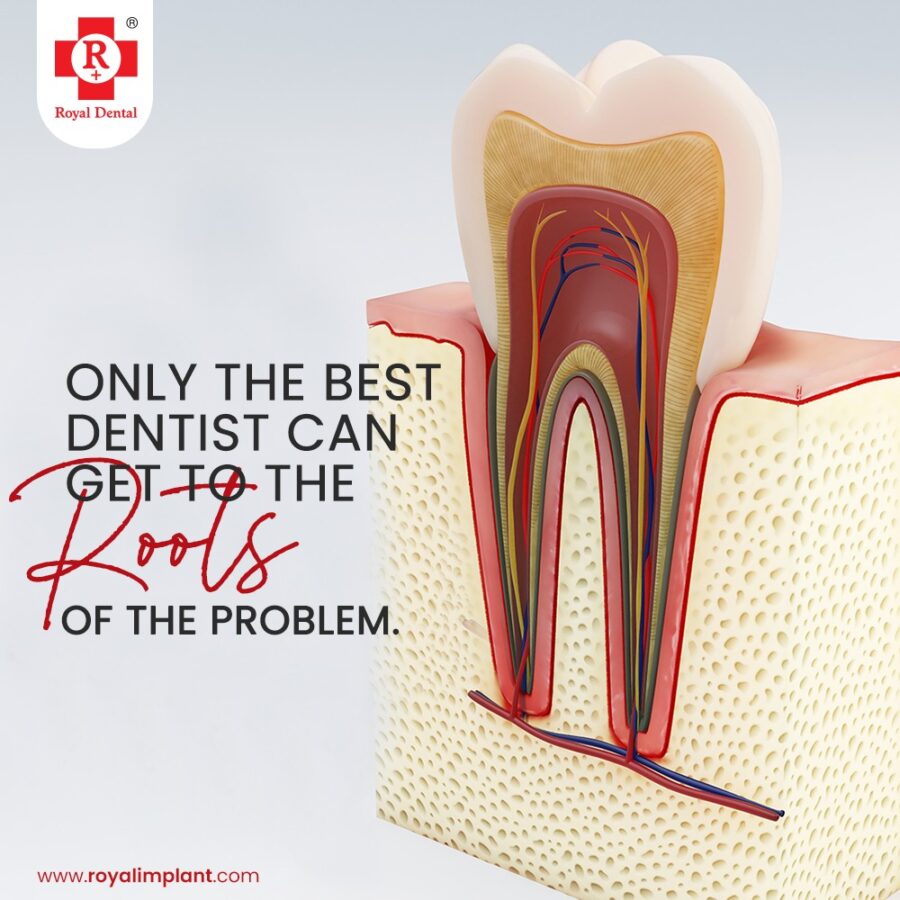
Excess blood flow in pulp
Excess blood flow to the pulp gives rise to hyperaemia. This is a result of gingival recession causing exposure of the root of the tooth and dissolved cementum. The pulp consists of blood vessels and nerve tissue, which when inflamed due to bacterial infection causes pulpitis. The excess blood flow cause widening of blood vessels that is vasodilatation. Which may also leads to the tooth pain in future but without clinical signs of cavity.
If there is no sign of a cavity, yet there is tremendous tooth pain, then there are chances you may need to visit your dentist. A sinus infection, is a less common but significant cause of toothache.
Hyperaemia toothache
The tooth in general is sensitive to heat and cold due to increased amount of blood flow. It is also sensitive too sweet food. Such teeth show no clinical caries when examined. Hyperaemic tooth shows two types of changes in the pulp;
Reversible pulpitis is of mild nature. The inflammation in such cases mild and the tooth saved as the pulp remains healthy. In reversible pulpitis, the pain disappears after seconds. The pulp able to heal when the irritation factor removed. This not seen in case of irreversible pulpitis.
Irreversible pulpitis causes severe pain wherein the pulp cannot be saved and the tooth goes into a root canal treatment or if delayed further then an extraction of that tooth. The pulp is surrounded by dentin. Therefore, there is no way for the pressure created to dissipate, the increased blood flow will result in pain.
The causes of Hyperaemia could be:
Intentional crown preparation done to a healthy tooth, which acts as an abutment.
Trauma to the tooth which may lead to thin fracture in enamel.
Deep scaling procedures affecting to the root.
Root caries in close proximity to the pulp.
Orthodontic wires create pressure to teeth causing blood flow changes.
The hyperemic tooth is sensitive to touch. There is always a dull or throbbing pain associated around tooth. There is a raise of body temperature too. Hyperemic tooth can be prevented by :
- Brushing twice a daily along with flossing
- Avoid sugary, starchy food
- Visiting your dentist for fluoride treatments
- Replace your toothbrush every 3 months
- Scaling and polishing of teeth twice every year.
However, if your teeth suddenly become sensitive or feel painful, don’t wait, make an appointment with your dentist. A simple check up or a minor treatment can often eliminate the discomfort quickly and prevent future pain. Above all, regular preventative treatment such as dental cleanings and examinations can allow dentists and hygienists to detect problems early and solve them using the most conservative methods possible.

Don’t ignore these symptoms, see your dentist right away:
Firstly, Moderate to severe toothache that lasts for more than 48 hours
Secondly, Throbbing or sharp, aching pain that won’t let up
Migraine or pounding headache that extends to your teeth
Fever that seems to coincides with a toothache
Above all, Swelling in your mouth or of your jaw.
Conclusion
Active hyperaemia or toothache is a physiological response to something happening in the body. It is an acute form of hyperemia. For example, there is more blood in the digestive system after a meal, more blood in the muscles after exercise, and more blood in the face when a person blushes.
Follow Us For More Updates




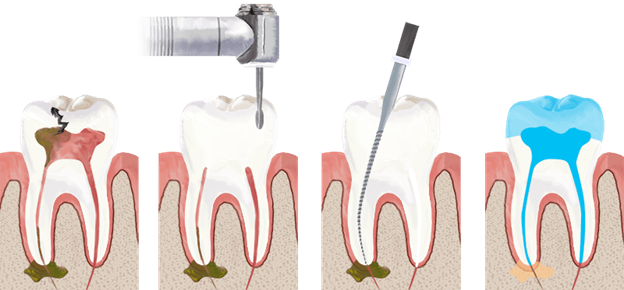
That’s truth. dental checkup will helps your oral health’s problem.