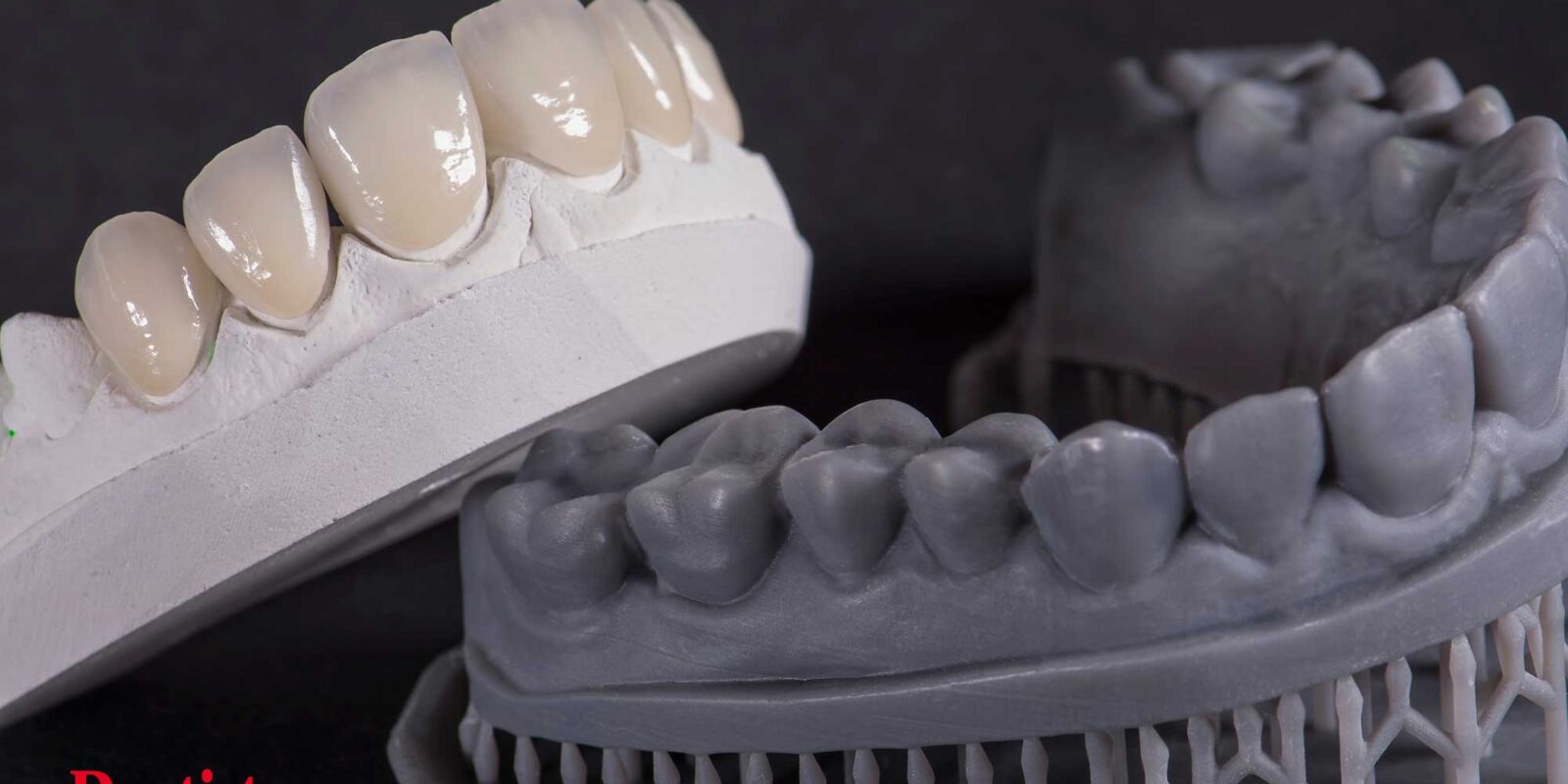
Yes, 3D printing is considered part of Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM). CAM encompasses various technologies and processes that utilize computer systems to assist in the manufacturing of physical objects. 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves creating three-dimensional objects by layering materials based on a digital design. Therefore, 3D printing is a form of manufacturing that falls under the umbrella of CAM. In this article, Dr. Chirag Chamria, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon at Royal Dental Clinics, delves into the fascinating world of 3D printing and its integration with Computer-Aided Manufacturing in dentistry.
Understand Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
CAM Software and its Functionality: CAM software converts design files into machine-readable instructions. The programmed optimizes toolpaths by considering material qualities, tooling alternatives, and machining settings. Optimizing machining methods reduces waste and boosts efficiency.
Integration with Computer-Aided Design (CAD): CAD software supports CAM. CAD software creates digital models of products and components. CAM uses geometric data from the CAD model for machining.

Different CAM Processes: CAM encompasses a range of manufacturing processes, including milling, turning, grinding, and other subtractive manufacturing methods. Let’s see some of these processes: milling, turning and grinding.
CAM in Various Industries: CAM finds applications in a wide range of industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics. Here are a few examples: aerospace, automotive, medical and electronics.
Advancements in CAM: CAM technology continues to evolve, driven by advancements in software capabilities, machine tools, and materials. Some notable advancements include:
- Multi-axis Machining
- Simulation and Verification
- Integration with Additive Manufacturing
Rise of 3D Printing in Dentistry
Dentistry has been transformed by it. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, uses computer designs to layer material to create three-dimensional items. It in dentistry improves accuracy, efficiency, and patient experience. It has affected the following:
Prosthetics and Restorations: 3D-printed crowns, bridges, and dentures fit. CAD software creates personalised restorations from patient mouth pictures. Biocompatible 3D printers make these designs. Eliminating manual modelling increases turnaround and patient comfort.
Surgical Guides: They are often made using it in implant dentistry. Custom guidelines help dentists place dental implants accurately. 3D-printed surgical guides help dentists correctly place, angle, and depth implants, improving surgical results and reducing risk.
Orthodontics: It makes transparent aligners like Invisalign possible, revolutionising orthodontics. It can manufacture personalised aligners that progressively reposition a patient’s teeth. Traditional braces are less comfortable, convenient, and attractive than this technology.
Integrating 3D Printing with CAM in Dentistry
3D printing and CAM in dentistry improve workflow and capacities. CAM systems generate toolpaths to automate manufacturing when combined with CAD software. It may benefit the dentistry profession. Dental 3D printing and CAM integration benefits:
Streamlined Workflow: Dental labs and clinics may streamline the design-to-production process by combining it with CAM. CAD software creates dental restorations, while CAM systems programmed 3D printers and milling equipment. This connection saves time and minimizes manual procedures.
Hybrid Manufacturing: Dental restorations need metal frames and ceramic crowns. Hybrid repairs using 3D printing and CAM integration are conceivable. A 3D printer can make a metal structure, and CAM can mill the ceramic overlay for a precise, lasting output.


Customization and Personalization: They enable dental application customization and personalisation. Dental restorations are customised to each patient’s anatomy and needs. CAM technologies provide perfect fit and function, while 3D printing allows complex and highly customised shapes.
Rapid Prototyping and Iteration: CAM-integrated 3D printing allows quick prototype and iterative design. Dentists and technicians may swiftly make physical models and prototypes to test restoration fit, function, and aesthetics. Digital design iterations and their production reduce trial-and-error time and expense.
Automation and Precision: CAM systems provide accurate milling toolpaths for dental restorations. Automation and accuracy provide consistent, high-quality output. Automated CAM procedures may run overnight or during non-working hours, increasing productivity and lowering manufacturing time.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Dentistry
Enhanced Precision and Accuracy: It makes exact dental restorations. Dental experts may create exact restorations utilizing computerized images of patients’ mouths. Precision improves prosthesis fit, patient comfort, and treatment results.
Customization and Personalization: It lets dental restorations be personalised. 3D printing lets dentists customize restorations to each patient’s oral anatomy. Customization optimizes fit, function, and aesthetics.
Time and Cost Efficiency: 3D printing has cut dental restoration time and expense. Traditional production involves human labour, many processes, and dental lab outsourcing. 3D printing allows in-house production, eliminating outsourcing and speeding up turnaround. Efficiency helps dentists and patients.
Improved Patient Experience: Dental patients benefit from it. Patients may avoid painful impression materials with digital scanning and 3D printing. 3D-printed restorations save dental visits and chair time due to its speedier turnaround and precision.
Dental Education and Training: Dental training has benefited from 3D printing. It can create anatomical models for dental students to practise operations. This technology helps dental practitioners practise before treating patients.
Applications of 3D Printing in Dentistry
The versatility of 3D printing has opened up a wide range of applications in the field of dentistry, expanding treatment possibilities and improving patient outcomes.
Dental Models and Surgical Guides: It enables the creation of accurate dental models and surgical guides, aiding in treatment planning and implant placement.
Orthodontic Aligners: It allows for the fabrication of clear aligners, revolutionizing orthodontic treatment by providing comfortable, discreet, and customized solutions.
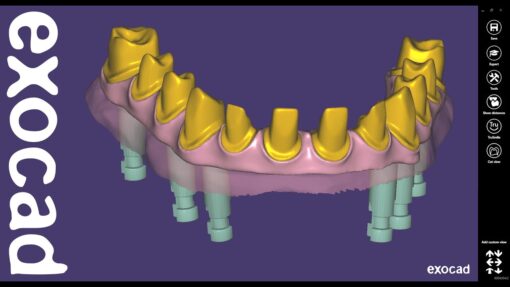
Prosthetic Restorations: It facilitates the production of crowns, bridges, dentures, and other prosthetic restorations with exceptional precision and aesthetics.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Implants: It has emerged as a promising technique for the production of patient-specific TMJ implants, improving functionality and patient comfort.
Future Prospects | 3D printing
The future prospects of 3D printing in dentistry are promising, with ongoing advancements and innovations that will continue to transform the field. Here are some key future prospects for it in dentistry:
Biocompatible Materials: Biocompatible dental materials are being developed. These materials improve strength, durability, and aesthetics, making them suitable for more dental restorations. Materials that mimic natural teeth are stronger and more natural-looking.
Multimaterial Printing: Multiple-material it brings up new dental uses. Dentists may use many materials to create complicated dental restorations. Combining hard and flexible materials in a restoration improves functionality and patient comfort.
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Dentistry: It might help tissue engineering and regenerative dentistry. 3D-printed scaffolds are being investigated for periodontal, bone, and tooth regeneration. This may lead to novel dental restoration methods.
Point-of-Care Manufacturing: Point-of-care manufacturing at dental clinics is possible as 3D printing technology gets more compact, inexpensive, and user-friendly. Dentists may be able to make dental restorations, surgical guides, and other equipment in-house, decreasing outsourcing and boosting treatment efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing has undoubtedly become an essential component of Computer-Aided Manufacturing in dentistry. Its ability to fabricate precise and patient-specific dental restorations has transformed the field, allowing dental professionals to provide enhanced treatments with improved accuracy and efficiency. With ongoing advancements and increasing adoption, it is set to shape the future of dentistry, revolutionizing the way oral healthcare is delivered. Remember, at Royal Dental Clinics, we are committed to staying at the forefront of technological advancements to ensure that our patients receive the highest quality care. Contact us to experience the benefits of advanced dentistry powered by 3D printing and Computer-Aided Manufacturing.
© All rights reserved by Royal Dental Implants Pvt Ltd
Issued in public interest