When it comes to oral care and the prevention of disease, most people think of good habits like brushing your teeth and flossing. However, there are several other factors that come into play that many people may not be aware of. One of these is something called gingival recession, or what is commonly referred to as gum recession or receding gums. The gums are the soft tissues that surround your teeth on their outer edges. When the gums recede, they become weak and begin to pull away from the teeth. This opens up access for bacteria to get beneath them and leads to food being trapped causing infections. Implant treatment is also possible in gum issues. To help you better understand how this impacts your oral health, here is a brief explanation.
What is gum implant disease?
Gum implant disease refers to when the gums begin to recede away from the teeth due to a variety of factors. This is usually caused by the gum tissues being weakened and becoming unable to retain their normal position around the teeth and being less effective at performing their normal healing abilities. As gum tissues become weak, they begin to pull away from the teeth. This leaves more area between the teeth and gums, causing bacteria to collect underneath the gums and leading to periodontal disease and increased risk of infection.
It is possible to have gum implant disease without experiencing any pain or sensitivity. However, this may also be a sign of tooth decay or another problem that needs to be looked into further. You can have implant gum disease and not even know it until you go in for a dental exam and X-rays reveal that your gums have receded behind the teeth and bacteria has developed below them.
Causes of implant gum diseases
Similar to gum disease, implant gum disease is caused by colonization of hundreds of different bacterial species on the crown, abutment, and surface of implant screw. When this occurs. It is usually more difficult to decontaminate dental implant, because screw surfaces are intentionally made to be rough to encourage in-growth of jaw bone, providing better integration between implant and jawbone. Risk factors for implant gum disease are as follows:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Lack of regular implant cleaning appointments
- Medical conditions (e.g. uncontrolled diabetes)
- Smoking
- Residual cement left on the surface of implant by the restorative dentists during implant crown cementation
What causes gum recession?
The root causes of gum recession are varied, with genetics playing a large role. A diet low in nutrients and high in processed foods, tobacco use. And excessive alcohol consumption are also common causes of gum recession. Poor oral hygiene habits. Such as not brushing your teeth twice daily and flossing regularly, can also contribute to gum recession. Poor oral hygiene habits can lead to gum disease, which can cause gum recession. Gum disease is an infection of the gum tissue around your teeth.
It is caused by bacteria that are often found around teeth and in the mouth. Some people are more likely to get gum disease than others. This may be because they have certain health conditions or have dental work done. Certain medications can also make it more likely. Gum disease can lead to gum recession, which is when the gums separate from the teeth. This is often seen as a line of slight bleeding when brushing. This can leave you more at risk of tooth and bone loss. Gum disease can also cause bad breath, gingivitis, and other oral health problems.
How can you tell if you have gum implant disease?
If you are experiencing any of the above symptoms or have noticed an increased amount of gum tissue bleeding when brushing, you may want to see your dentist for an evaluation. You may be experiencing gum recession. If so, it is important to be evaluated for potential causes as gum recession may be a sign of an underlying health issue.
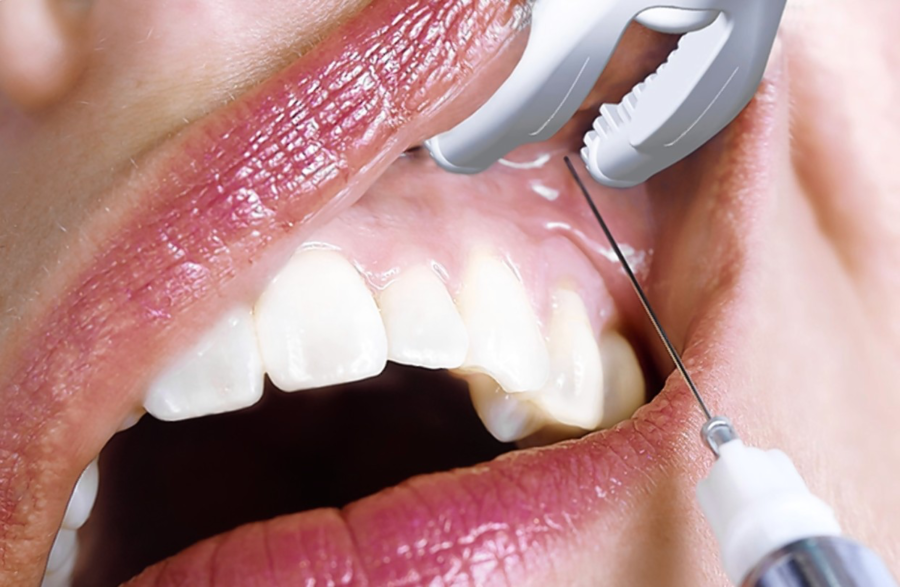
A dental exam is a good first step in determining if you have gum recession. Your dentist will take X-rays of your teeth and gum line to look for any signs of gum recession including open pockets. Exposed root surfaces, and bone loss. They may also look for signs of certain gum diseases such as gingivitis or periodontitis.
Treatments for gum recession
- Periodontal maintenance – This is simply a good oral hygiene routine to keep the gums healthy and bacteria free. This can include daily brushing and flossing. Regularly changing your toothbrush is recommended every three months.
- Vitamin supplements. Vitamin supplements can help strengthen the gum tissues and reverse the damage caused by gum recession. A Vitamin C and E are the most effective. Vitamin E has been proven to boost the healing properties of gum tissue and help reverse the damage associated with gum recession.
- Dental sealants – Dental sealants are used to prevent food from being trapped between the teeth and around the gum line.
- Gum grafts – Gum grafts are a procedure that reattaches the gum tissues to the teeth. This is usually done when a tooth has become loose due to gum recession.
Conclusion
Gum disease can be a serious problem if not treated. And those who have gum recession are more at risk of contracting it. If you notice that your gums are bleeding more than usual when brushing your teeth. You might be experiencing gum recession. Visit your dentist to have them look into the cause and recommend treatment as soon as possible to prevent gum disease. Keeping your gums healthy is important for your oral health.






