Hello, and thank you for visiting the Royal Dental Clinics’ blog, where we want to dispel some of the misconceptions around dental care and give you accurate information. This article answers a common concern about teeth whitening: does it take away a little bit of enamel? Patients worry about the effectiveness and durability of teeth-whitening treatments. We sought the expertise of Dr. Chirag Chamria, a dentist at Royal Dental Clinics, to help us sort reality from fiction in your smile matter.
Understanding Teeth Whitening
Teeth whitening is a cosmetic dental procedure that aims to remove stains and discoloration from the teeth, resulting in a brighter and more attractive smile. It has gained significant popularity in recent years as people increasingly seek ways to enhance their appearance and boost their confidence.
Causes of Tooth Stains
Extrinsic Stains: These are stains that affect the outer layer of the tooth, known as the enamel. Extrinsic stains are often caused by consuming certain foods and beverages (such as coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored fruits), smoking or using tobacco products, and inadequate oral hygiene practices.
Intrinsic Stains: Intrinsic stains are located within the tooth’s structure and can be caused by factors like aging, trauma, certain medications (such as tetracycline), excessive fluoride exposure during tooth development, or underlying dental conditions.
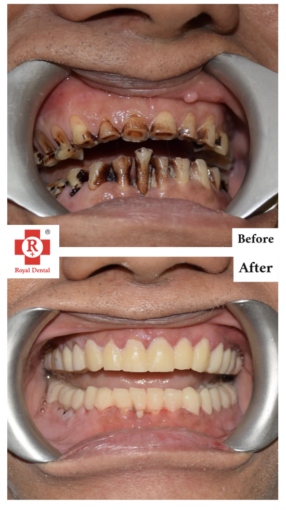
How Teeth Whitening Works
Teeth whitening procedures work by using agents that penetrate the enamel and break down the stains or discoloration. The most common active ingredient in teeth-whitening agents is hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide.
When these peroxide-based agents come into contact with the teeth, they release oxygen molecules that penetrate the enamel and target the discolored molecules within the tooth’s structure. This chemical reaction breaks down the stains, resulting in a lighter appearance.
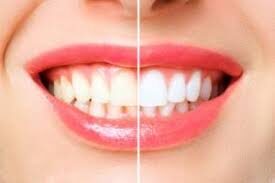
Professional In-Office Whitening
Professional in-office teeth whitening is a popular option that provides fast and noticeable results. This procedure is performed by a qualified dentist or dental hygienist in a dental office.
During an in-office whitening treatment, a protective barrier is applied to the gums, and a concentrated whitening gel is applied to the teeth. The gel is usually activated by a special light or laser, which helps accelerate the whitening process. The treatment is typically completed in one or a few sessions, with each session lasting about 30 to 60 minutes.
At-Home Whitening Kits
At-home teeth whitening kits are an alternative option for those who prefer the convenience of whitening their teeth in the comfort of their own homes. These kits usually consist of custom-fitted trays and whitening gel.
To use an at-home whitening kit, the patient fills the trays with the whitening gel and wears them for a specified period, as directed by the dentist. The duration of the treatment can vary depending on the desired level of whitening and the concentration of the whitening gel. At-home whitening kits generally take longer to achieve noticeable results compared to in-office treatments.
Over-the-Counter Whitening Products
In addition to professional treatments, there is a wide range of over-the-counter teeth-whitening products available, including whitening toothpaste, strips, gels, and rinses. These products typically contain lower concentrations of whitening agents compared to professional treatments.
While over-the-counter whitening products can provide some improvement in tooth color, they may not be as effective as professional treatments. It’s important to carefully follow the instructions provided and consult with a dentist if you have any concerns or questions.
Safety Considerations
Teeth whitening, when performed under the supervision of a dental professional, is generally safe. Dentists take into account factors such as the patient’s oral health, sensitivity levels, and desired results to determine the most appropriate whitening method.
Composition of Teeth
Enamel: Outermost layer, composed mainly of hydroxyapatite, provides protection and contributes to the white color of teeth.
Dentin: Located beneath enamel, yellowish tissue that forms the bulk of the tooth, less mineralized than enamel.
Pulp: Innermost part, soft living tissue with blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue, responsible for supplying nutrients and sensation.
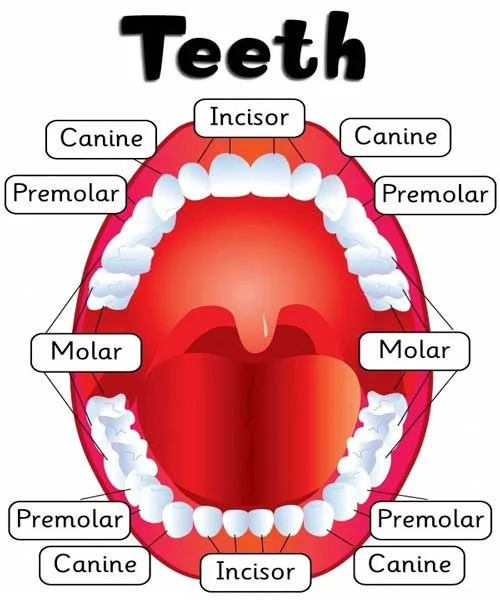
Cementum: Thin calcified tissue covering the root surface, provides attachment for periodontal ligament fibers.
Periodontal Ligament: Fibrous tissue surrounding the tooth root, connects the tooth to the surrounding alveolar bone, acts as a cushion and shock absorber.
Alveolar Bone: Surrounds and supports the teeth, forms the sockets where teeth are anchored, crucial for stability and alignment of teeth.
Mechanisms of Teeth Whitening
Oxidation
The primary mechanism behind teeth whitening is oxidation. The peroxide-based whitening agents, such as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, release oxygen molecules when they come into contact with the teeth. These oxygen molecules penetrate the enamel and reach the discolored molecules present within the tooth structure.
The oxygen molecules react chemically with the chromogens, which are responsible for the stains or discoloration, breaking them down into smaller, less pigmented molecules. As a result, the teeth appear brighter and whiter.
Penetration and Diffusion
Teeth whitening agents need to penetrate the enamel to reach the underlying dentin, where the discoloration occurs. The peroxide molecules in the whitening agents have small molecular sizes, allowing them to penetrate the porous enamel layer.
Once inside the enamel, the peroxide molecules diffuse through the enamel and into the dentin, where they can break down the stains effectively. This process takes time and may require repeated applications of the whitening agents to achieve the desired level of whitening.
Chemical Breakdown of Stains
As the peroxide molecules reach the dentin, they initiate a chemical breakdown of the stains or discoloration. Peroxide acts as a bleaching agent by oxidizing the chromogens and altering their molecular structure. This breakdown reduces the intensity of the discoloration, resulting in a lighter tooth color.
The duration of contact between the whitening agent and the tooth surface is crucial for achieving optimal results. Professional in-office whitening treatments often utilize stronger concentrations of peroxide and may involve the use of light or laser activation to enhance the effectiveness of the chemical breakdown process.
Free Radical Formation
During the oxidation process, the peroxide molecules release free radicals, which are highly reactive oxygen species. These free radicals play a significant role in breaking down the chromogens and removing the stains from the teeth.
The free radicals generated by the peroxide molecules are unstable and quickly react with the colored molecules, altering their chemical structure and rendering them colorless or less pigmented. This reaction contributes to the overall whitening effect.
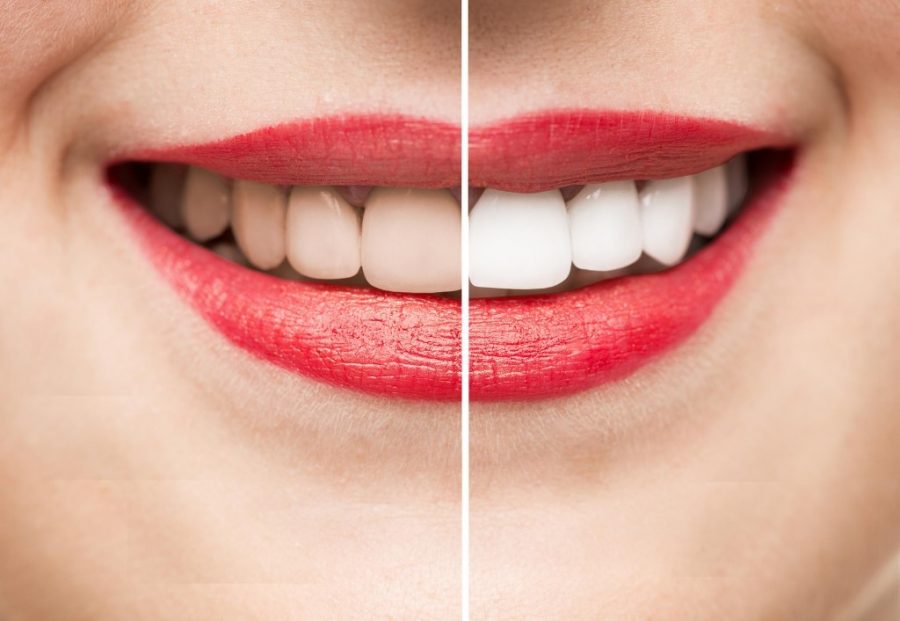

Time and Concentration
The effectiveness of teeth whitening depends on the concentration of the whitening agent and the duration of its contact with the teeth. Higher concentrations of peroxide generally provide more significant whitening results but may also increase the risk of tooth sensitivity or irritation.
Dentists carefully consider the patient’s oral health, sensitivity levels, and desired results to determine the appropriate concentration and treatment duration. Over-the-counter whitening products typically contain lower concentrations of peroxide to ensure a safer application for general use.
pH Balance
Teeth whitening agents also play a role in maintaining an optimal pH balance within the mouth. Whitening gels and solutions are formulated to be slightly acidic, helping to create an environment that facilitates the breakdown of stains and enhances the overall whitening process.
Role of Peroxide in Teeth Whitening
Peroxide plays a significant role in teeth whitening procedures. Peroxide, such as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, is the primary active ingredient in whitening agents. When applied to the teeth, peroxide undergoes a chemical reaction that leads to the release of oxygen molecules. These oxygen molecules penetrate the enamel and dentin, targeting the molecules responsible for tooth discoloration.
The peroxide molecules break down the chromogens, which are the colored compounds that cause stains on the teeth, by oxidizing them. This oxidation process alters the chemical structure of the chromogens, making them less pigmented or colorless. As a result, the teeth appear whiter and brighter.
The concentration of peroxide used in teeth whitening treatments can vary depending on the method and the severity of the stains. Higher concentrations of peroxide generally provide more noticeable whitening effects, but they may also increase the risk of tooth sensitivity or irritation. Therefore, it is important to follow the instructions provided by Dr. Chamria, to ensure safe and effective use of peroxide-based whitening agents.
Safety of Teeth Whitening to Smile
Teeth whitening is generally considered safe when performed under the supervision of a qualified dentist. However, it is important to follow proper guidelines and precautions. Temporary tooth sensitivity and gum irritation are common side effects that typically subside after treatment. Using professional-grade whitening products and following recommended treatment durations and frequencies can help minimize risks. Individuals with pre-existing dental conditions should consult with their dentist before undergoing whitening. Overall, by seeking professional supervision and adhering to recommended practices, teeth whitening can be a safe and effective way to enhance your smile.
Potential Side Effects
Tooth Sensitivity: Teeth whitening often causes tooth sensitivity. Peroxide-based whitening treatments might make teeth more sensitive to heat and cold. After therapy, sensitivity generally decreases. Dentist-recommended desensitizing toothpaste or gels may relieve pain.
Gum Irritation: Whitening products may temporarily irritate gums. Avoid excessive gum tissue contact by carefully following your dentist’s or product manufacturer’s recommendations. Dentists utilize protective barriers or custom-fitted trays to reduce gum discomfort during in-office procedures.
Uneven Whitening: Teeth may whiten unevenly. If the whitening chemical is administered unevenly or if some teeth have greater discolouration than others, this might happen. Professional monitoring and individualized treatment strategies may reduce uneven whitening and improve outcomes.

Enamel Erosion: Use of teeth whitening products, particularly those with high whitening chemical concentrations, might cause enamel degradation. It increases tooth sensitivity and damage. Follow your dentist’s advice and treatment length and frequency.
Gum and Tooth Sensitivity Precautions: Tooth sensitivity, gum disease, and exposed tooth roots may make teeth whitening uncomfortable. Your dentist will assess your dental health and suggest precautions or alternatives to reduce side effects.
Maintaining Whitened Teeth Smile
- Practice good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth at least twice a day and flossing daily.
- Limit the consumption of staining foods and drinks like coffee, tea, red wine, and berries.
- Use a straw when drinking staining beverages to minimize contact with your teeth.
- Quit tobacco use to prevent severe staining.
- Rinse your mouth with water after consuming staining substances.
- Consider touch-up whitening treatments as recommended by your dentist.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings to monitor the health of your teeth and address any discoloration.
- Follow any additional maintenance recommendations provided by your dentist to maintain your whitened smile.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the myth that teeth whitening removes a thin layer from your teeth is just that—a myth. Teeth whitening procedures are designed to break down stains and discoloration within the teeth, without compromising the integrity of the tooth structure. With proper dental supervision and adherence to recommended guidelines, teeth whitening is a safe and effective way to enhance the appearance of your smile. At Royal Dental Clinics, our experienced dentist, Dr. Chirag Chamria, prioritizes patient safety and satisfaction. If you’re considering teeth whitening or have any concerns about your dental health, we encourage you to schedule a consultation with us. Remember, a bright, confident smile starts with accurate information and professional care.
© All rights reserved by Royal Dental Implants Pvt Ltd
Issued in public interest






