Dentistry is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on oral health and the treatment of dental issues. Dentist are highly trained doctor who undergo rigorous education and clinical training to provide oral health to patients. However, a common question that often arises is whether dentists qualify as doctors. In this article, we will delve into this topic and explore the qualifications and expertise of dentists. To provide valuable insights, we will refer to the expertise and knowledge of articles.
Education and Training Requirement | Dentist Doctor
Education and training requirements for dentists are crucial components in their journey to becoming qualified professionals in the field of dentistry. Let’s explore this aspect in more detail.
Dentists are required to complete a rigorous educational program that includes both classroom instruction and clinical training. The specific requirements may vary slightly depending on the country or region, but the overall framework remains consistent.
Pre-Dental Education
Before entering dental school, aspiring dentists typically complete a bachelor’s degree in a science-related field. While dental schools may accept students with various undergraduate majors, most applicants choose to pursue degrees in biology, chemistry, or other natural sciences. This foundational education provides a strong basis for the scientific principles and concepts that dentistry entails.
Dental School
After completing their bachelor’s degree, aspiring dentists must gain admission to an accredited dental school. Dental school programs generally span four years, during which students undergo intensive training to develop the necessary knowledge and skills to practice dentistry.
Dental school curriculum covers a wide range of subjects, including anatomy, physiology, dental radiology, dental materials, oral pathology, dental pharmacology, and dental techniques. Students also gain practical experience through laboratory work and clinical rotations. This hands-on training allows them to apply their theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios, under the guidance of experienced faculty members.

Clinical Training Dentist Doctor
Clinical training is a vital component of a dentist’s education. Dental schools provide opportunities for students to work directly with patients, supervised by faculty members and experienced dental professionals. During this phase, students learn and practice various dental procedures, such as teeth cleanings, fillings, extractions, root canals, and prosthetic work.
Licensing Examinations
Upon completing dental school, graduates must obtain a license to practice dentistry legally. The licensing requirements vary from country to country, and sometimes even between states or provinces within a country. Typically, aspiring dentists need to pass a national or regional licensing examination that tests their knowledge and clinical competency. These examinations assess the graduates’ ability to diagnose oral conditions, develop treatment plans, and execute dental procedures safely and effectively.
Postgraduate Specialization (Optional)
After completing dental school and obtaining a general dentistry license, dentists may choose to pursue additional training in a specialized area of dentistry. Specialization allows dentists to focus on specific aspects of dental care, such as orthodontics, periodontics, endodontics, oral and maxillofacial surgery, or pediatric dentistry. Postgraduate programs in these areas typically range from two to six years, depending on the specialization.
Continuing Education
Throughout their careers, dentists are encouraged to engage in continuing education to stay updated with the latest advancements in dental research, technologies, and treatment modalities. This ongoing professional development ensures that dentists provide the highest quality care and remain competent in their practice.
Scope of Practice in Dentistry | Dentist Doctor
The scope of practice in dentistry encompasses a wide range of responsibilities and procedures that dentists are qualified to perform. Dentists play a vital role in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of various oral health conditions. Let’s explore the scope of practice in dentistry in more detail:
Preventive Care: Dentists’ major duty is preventative care. Dentists teach patients about brushing, flossing, and dental checkups. Professional teeth cleanings, tartar removal, and fluoride treatments may prevent tooth decay. Dentists recommend healthy diets and lifestyles for dental health.
Restorative Dentistry: Restorative dentistry fixes broken or missing teeth. Dentists may repair cavities, crown damaged teeth, and replace missing teeth with bridges or implants. Dentures or partial dentures may be offered to restore oral function and aesthetics.
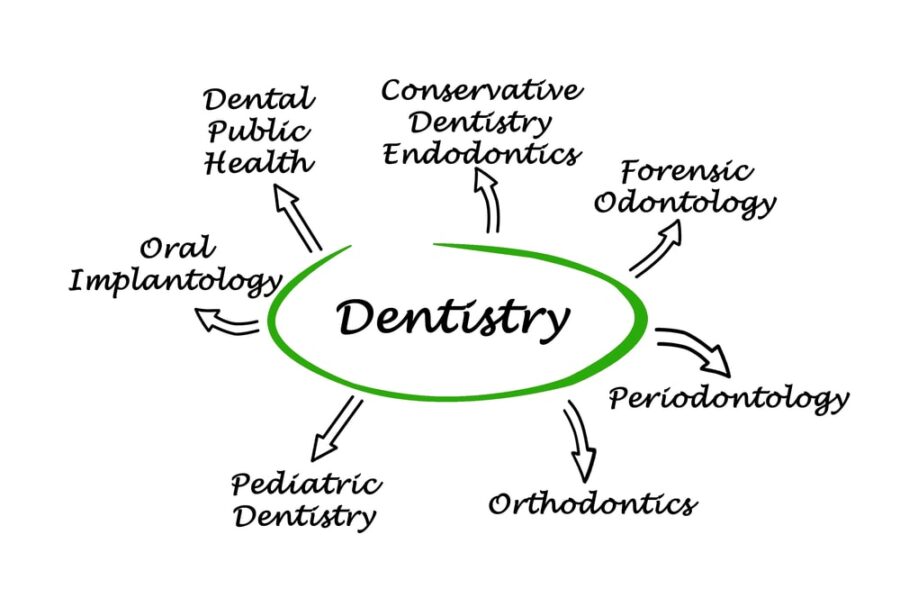
Endodontics: Endodontists treat pulp and root canal problems. They seal a tooth after root canal treatment to avoid infection. Endodontists are root canal specialists who can handle complicated situations.
Periodontics: Periodontics prevents, diagnoses, and treats gum disorders. Scaling and root planning help gums by removing plaque and tartar below the gumline. They may also advise on gum disease prevention and management.
Orthodontics: Orthodontic dentists fix misaligned teeth and jaws. They may suggest braces, aligners, or retainers to straighten teeth and jaws. Orthodontists collaborate with patients to plan and track therapy.
Oral Surgery: Dentists may remove teeth, including wisdom teeth. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons may perform dental implant implantation or corrective jaw surgery.
Continual Professional Development | Dentist Doctor
Continual professional development is a vital aspect of a dentist’s career, ensuring that they stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in dental research, technology, and treatment modalities. Let’s explore the importance and various aspects of continual professional development for dentists:
Staying Current with Research and Evidence-Based Practices: Evidence-based dentistry changes. Dentists continue their education. They may provide patients cutting-edge therapies. Conferences, seminars, and workshops teach dentists how to employ new technology, materials, and practices.
Enhancing Clinical Skills and Techniques: Continuing education helps dentists improve clinically. Hands-on seminars and workshops teach dentists new techniques and patient-friendly ways. This lets them provide patients cutting-edge dental care.
Ethical and Professional Responsibility: Professional growth includes ethics and responsibilities. Dentists must uphold ethical standards and follow changing industry rules. Dentists may learn about their legal, ethical, and patient rights by taking ethics and practise management courses.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration | Dentist Doctor
Interdisciplinary collaboration is a crucial aspect of providing comprehensive and holistic patient care in dentistry. Dentists often work closely with other healthcare professionals from different disciplines to ensure that patients receive the best possible treatment and outcomes. Let’s explore the importance and benefits of interdisciplinary collaboration in dentistry:
Comprehensive Treatment Planning: They may construct medical-dental treatment plans alongside other healthcare practitioners. Doctors and dentists may treat systemic diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular disease with oral symptoms. This holistic approach improves treatment.
Optimized Oral and Overall Health: Oral health impacts the body. Doctor, nutritionists, psychiatrists, and dentists may work together to establish full treatment plans. This method addresses oral and systemic health. They can improve patient health by seeing the whole picture.
Enhanced Patient Experience and Care Coordination: Interdisciplinary teamwork promotes a patient-centered, coordinated experience. They may coordinate care across specialisations by working with other healthcare providers. This reduces redundancy, contradictory treatment suggestions, and patient experience.
Research and Knowledge Sharing: Interdisciplinary cooperation fosters healthcare research and information sharing. They might incorporate the newest findings from different professions to their practise. This exchange of ideas and information advances dental treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dentists undoubtedly qualify as doctors. They undergo extensive education and training to acquire a doctoral degree in dentistry and meet licensing requirements to practice legally. Dentists possess the knowledge and skills necessary to diagnose, treat, and prevent oral health conditions. Their continual professional development and interdisciplinary collaboration highlight their commitment to delivering comprehensive care. As a vital part of the healthcare community, dentists play a crucial role in ensuring the oral health and overall well-being of their patients.