Hello, and thank you for visiting the Royal Dental Clinic’s blog page! As a dentist, Dr. Chirag Chamria aims to provide you with valuable information and insights into various aspects of dental health. In this article, we will explore the different types of dental X-rays, an essential diagnostic tool in modern dentistry. By understanding the various types of dental X-rays and their purposes, you can gain a better understanding of their importance in maintaining optimal oral health. Knowing the different forms of dental X-rays for mouth might help you grasp its value in oral health for adults and kids.
Why are Dental X-rays important?
Dental X-rays are important because they can help dentists detect and diagnose a range of dental issues that may not be visible during a dental exam. These issues can include cavities, gum disease, cysts, tumors, and impacted teeth. Dental X-rays can also help dentists plan treatments such as braces, implants, and dentures.
There are several advantages to getting dental X-rays. They are painless, non-invasive, and provide quick results. Dental X-rays are also relatively safe, with minimal radiation exposure. The benefits of dental X-rays far outweigh the risks, and they are an essential tool for maintaining good oral health.
Types of Dental X-rays | Oral Health
There are two main types of dental X-rays: intraoral and extraoral. Intraoral X-rays are taken inside the mouth, while extraoral X-rays are taken outside the mouth. Each type of X-ray provides a different view of the teeth and jaw, allowing dentists to diagnose and treat dental issues more effectively.
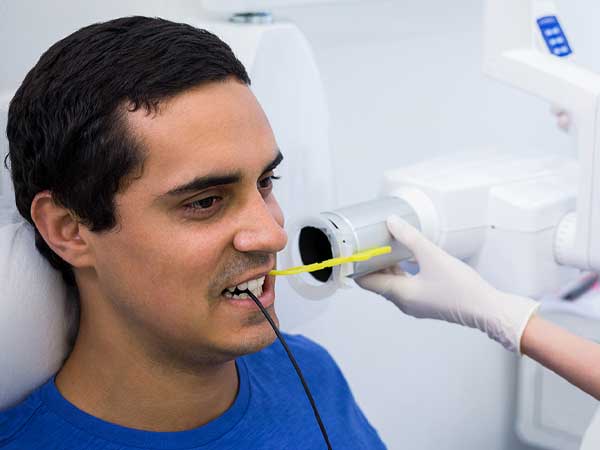
Intraoral x-rays
Intraoral X-rays are the most common type of dental X-ray. They provide a detailed view of the teeth, bone, and supporting tissues inside the mouth. There are several types of intraoral X-rays, including bitewing, periapical, and occlusal X-rays.
Bitewing X-rays
Bitewing X-rays are the most common type of intraoral X-ray. They are used to detect cavities between teeth and to monitor bone loss caused by gum disease. Bitewing X-rays show the upper and lower teeth in a specific area of the mouth. They are often used during routine dental check-ups to check for early signs of dental decay.
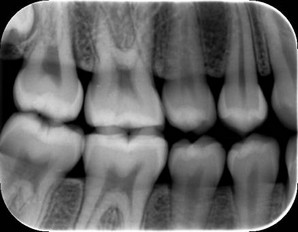
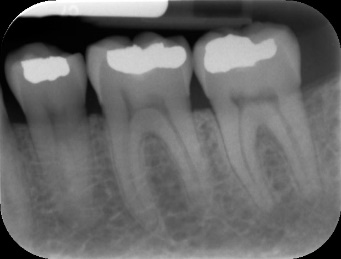
Periapical X-rays
Periapical X-rays provide a detailed view of one or two teeth from root to crown. They are used to detect dental issues such as abscesses, cysts, and tumors. Periapical X-rays are also used to monitor the progression of certain dental treatments, such as root canal therapy.
Occlusal X-rays
Occlusal X-rays are used to examine the roof or floor of the mouth. They are often used to detect extra teeth, teeth that have not yet erupted, or abnormalities in the jawbone. Occlusal X-rays are also used to examine the overall development of a child’s teeth and to plan orthodontic treatment.
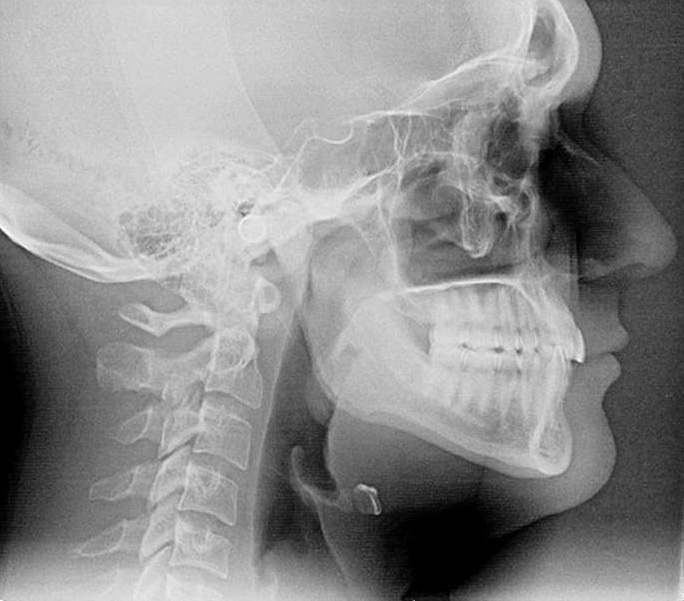
Extraoral x-rays
Extraoral X-rays are taken outside the mouth and show the teeth, jaw, and skull. They are used to detect issues such as impacted teeth, jaw disorders, and tumors. There are several types of extraoral X-rays, including panoramic X-rays and cone beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Panoramic X-rays
Panoramic X-rays provide a broad view of the entire mouth, including the teeth, jawbone, and sinuses. They are often used to detect impacted teeth, jaw disorders, and tumors. Panoramic X-rays are also used to plan orthodontic treatment and to evaluate the progression of certain dental treatments.
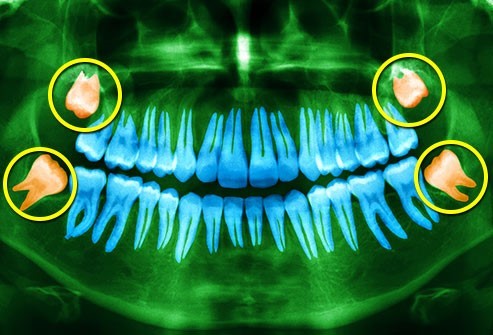

Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT)
CBCT provides a 3D view of the teeth, jaw, and skull. It is often used to plan dental implants, orthodontic treatment, and oral surgery. CBCT is more detailed than panoramic X-rays, and it provides a more accurate view of the teeth and jawbone.
Digital vs. Traditional Film X-rays | Oral Health
Digital X-rays are becoming increasingly popular in dental practices. They use a digital sensor to capture the X-ray image, which is then displayed on a computer screen. Digital X-rays are faster, more efficient, and produce less radiation than traditional film X-rays. They are also more environmentally friendly, as they do not require the use of chemicals to develop the X-ray film.
Traditional film X-rays, on the other hand, use X-ray film to capture the image. The film must be developed in a darkroom using chemicals. While traditional film X-rays are still used in some dental practices, they are becoming less common as digital X-rays become more prevalent.
Risks and Safety Considerations | Oral Health
Radiation Exposure: Dental X-rays involve exposure to ionizing radiation, albeit at a very low dose. The amount of radiation used in dental X-rays is significantly lower compared to other medical imaging procedures like CT scans or general X-rays. Nevertheless, repeated exposure over time can accumulate, so it’s important to minimize unnecessary X-rays and follow appropriate guidelines for their use.
Proper Technique and Equipment: Ensuring the use of appropriate techniques and well-maintained X-ray equipment is crucial for minimizing radiation exposure. Dentists and dental assistants should follow recommended protocols, including using the lowest possible dose of radiation and positioning the X-ray machine correctly.
Pregnancy Considerations: If a patient is pregnant or suspects they might be pregnant, it is important to inform the dental professional. X-rays, especially those involving the abdominal or pelvic region, are generally avoided during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary. In such cases, additional precautions may be taken to shield the fetus, such as using a lead apron with an abdominal shield.
Digital X-rays: Digital X-ray systems have become more prevalent in dental practices. These systems use electronic sensors instead of traditional X-ray films, significantly reducing radiation exposure. Digital X-rays also offer the advantage of immediate image acquisition, easier storage, and the ability to enhance and manipulate images for better diagnosis.
How often should you get Dental X-rays?
The frequency of dental X-rays depends on several factors, including your age, dental health, and risk of dental issues. Children may need X-rays more frequently than adults, as their teeth and jaw are still developing.
Generally, bitewing X-rays are recommended once a year, while panoramic X-rays are recommended every three to five years. However, this can vary depending on your individual needs. Your dentist will recommend the frequency of X-rays based on your dental health and risk of dental issues.
Conclusion
Dental X-rays are an essential part of dental care. They help dentists diagnose and treat a range of dental issues, from cavities to jaw disorders. By understanding the different types of dental X-rays and their uses, you can make informed decisions about your oral health. Talk to us about the frequency of X-rays that is right for you, and don’t hesitate to ask any questions or voice any concerns you may have. With the right care and attention, your smile can stay healthy and beautiful for years to come.
© All rights reserved by Royal Dental Implants Pvt Ltd
Issued in public interest