Dental caries (cavities) and plaque are two well-known monsters that pose a daily threat to the perfect state of your teeth. Despite their silence, these enemies are unrelenting in their attempts to ruin your dental health. Let’s set out on a quest to expose these offenders, comprehend their motivations, and learn the secrets of keeping a winning smile.
What are Dental Caries?
Dental caries, also referred to as cavities or tooth decay, is a cunning attack that assaults the structural integrity of your teeth. With its roots firmly planted in bacterial mischief, sugar-fueled sabotage, and the slow deterioration of oral defenses, this stealthy invader works in phases.
Causes of Dental Cavities
The role of Streptococcus mutant bacteria:
Streptococcus mutans is a tiny partner at the core of dental caries. Although they are not naturally harmful, these bacteria have an amazing capacity to change the carbohydrates in our meals into acids. They create acid as a metabolic byproduct when they gorge on sugars, particularly sucrose. This acid turns into a weapon that erodes your teeth’s protective enamel.
Impact of Sugar and Acid:
There is a complex relationship between sugar and dental caries. The Streptococcus mutans bacteria in your mouth feasts on sugars and turns them into acids when you indulge in sweets. Consequently, these acids attack the enamel and start the demineralization process. This continuous exposure erodes the enamel over time, fostering an atmosphere that is favorable for cavities to develop.
Stages of Development of Dental Caries
Enamel demineralization:
The demineralization of enamel, your teeth’s outer layer of protection, is a first sign of dental caries. The minerals that make up enamel begin to erode because of the acids produced when bacteria convert carbohydrates. Enamel is weakened by this process, increasing its vulnerability to further deterioration.
How Cavities Form:
The integrity of the enamel is weakened as demineralization advances, providing a pathway for the germs to enter the tooth structure and travel deeper. This is the point where cavities start to form. Cavities, which indicate the obvious signs of dental caries, are basically holes or cavities in the teeth. These cavities have the potential to grow and eventually reach the tooth’s inner layers if left untreated.
Possible Side Effects if Untreated:
Untreated dental caries have more negative effects than just a painful cavity. If the illness is allowed to worsen, a number of issues could develop: An infection can occur in the pulp, which is the tooth’s innermost layer. In order to save the tooth, this could cause excruciating pain and require root canal therapy.
Abscess Formation: If infections are left untreated, pockets of pus known as abscesses may form. These can cause excruciating pain and swelling. When the condition reaches a more advanced stage, extraction may be the only practical course of action due to the tooth’s reduced structural integrity. An increasing body of research is showing a connection between systemic health problems like diabetes and cardiovascular disease and oral health, particularly untreated dental caries.
What is Plaque?
Dental plaque enters the oral environment like a cunning saboteur and wreaks havoc. Its crucial role in maintaining dental health can be better understood by taking into account its composition, production, and the bacterial cooperation involved.

Understanding Dental Plaque
Content and Structure:
A biofilm known as dental plaque forms on the surfaces of teeth. It is a whitish, sticky coating made of saliva, germs, and leftover food particles. This film sticks to the teeth and becomes transformed into tartar, also called dental calculus, a more solid state if left unremoved.
Bacteria’s Place in the Development of Plaques:
Dental plaque is home to a wide variety of bacterial species, all of which have contributed to its creation. The same bacteria that causes tooth cavities, Streptococcus mutans, is one of the main offenders. These bacteria grow and produce materials that add to the plaque matrix while adhering to the tooth’s surface. Other bacteria, such as those linked to gum disease, join the microbial consortium as the plaque ages.
Impact on Oral Health
Relation to Periodontal Disease:
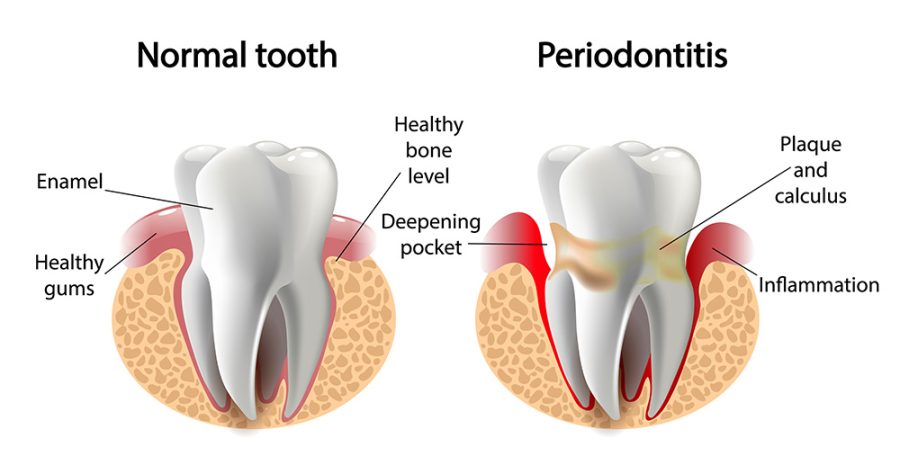
The effects of plaque on oral health go beyond dental cavities. Gingivitis is an inflammatory disorder of the gums that can be brought on by bacteria found in plaque. If gingivitis is not treated, it can develop into a more serious gum disease, such as periodontitis. Gum inflammation, bleeding, and redness are caused by the production of inflammatory chemicals by the immune system in reaction to the bacterial attack.
Plaque as a Dental Caries Progression:
Plaque contributes to the formation of cavities, much as Streptococcus mutans is the accomplice of dental caries. As the bacteria in plaque break down dietary carbohydrates, acid is produced. Dental caries is facilitated by this acid because it starts the demineralization process when it comes into contact with enamel. As a result, plaque serves as the starting point for the corrosive processes that erode enamel and cause cavities.
Distinguishing Features: Dental Caries vs Plaque
| Origin and Development | Dental Caries | Plaque |
|---|---|---|
| How Dental Caries and Plaque Initiate | The bacteria Streptococcus mutans enters the mouth and converts sugars into acids, which starts the demineralization process of enamel. This is how they starts. This compromises the tooth’s structural integrity by creating the conditions for the slow emergence of cavities. | Bacterial activity and surface adherence are more important factors. As it progresses, gingivitis may develop, and if left untreated, the bacteria in the plaque may release acids that demineralize the enamel, which may cause to cavities. |
| Key Differences in Their Progression | Cavities form as a result of the slow degradation of enamel that occurs with them. It mostly affects the tooth’s hard tissues, resulting in decay that is clearly evident. | It is mostly related to bacterial activity and surface adherence. As it progresses, gingivitis may develop, and if left untreated, the bacteria in the plaque may release acids that demineralize the enamel, which may cause to cavities. |
Dr. Chirag Chamria’s Insight
When starting a journey toward oral health, it’s quite beneficial to learn from experienced specialists like Royal Dental Clinics‘ Dr. Chirag Chamria. His expert viewpoint dismisses misconceptions about dental caries and plaque while providing patients with helpful advice.

An expert’s viewpoint on dental plaque and caries
Dr. Chamria emphasizes the value of taking a preventative stance. In order to prevent dental cavities and plaque, it is essential to have regular dental checkups, expert cleanings, and customized oral care regimens.
Dr. Chamria takes a comprehensive approach to oral health, understanding the relationship between dental caries, plaque, and general health. He promotes an in-depth comprehension of the relationship between oral health and lifestyle, nutrition, and dental hygiene habits.
Common Myths and Misconceptions Dispelled
Myth: Cavity-Free Is Equal to Sugar-Free:
Dr. Chamria explains that choosing sugar-free options is a good start, but it’s not a 100% guarantee against dental caries. Other important aspects are general nutrition and dental hygiene habits.
Irrespective of the common misconception that plaque is harmless, Dr. Chamria highlights that plaque serves as a marker for potential dental problems. Ignoring plaque can cause cavities to grow and can also result in gum disease.
Misconception: Plaque Does Not Cause Damage:
Dr. Chamria highlights the place of plaque as a forerunner to dental problems, refuting the common misconception that it is harmless. Ignoring plaque can cause cavities to grow and can also result in gum disease.
Practical Tips for Patients from Dr. Chamria’s Experience
Regular Dental Care:
Dr. Chamria promotes tooth brushing, flossing, and tongue cleaning as part of a regular dental care regimen. This is the cornerstone of a strong defense against dental cavities and plaque, together with routine dental checkups.
Attentive Nutrition:
He advises patients to take a balanced and attentive approach to nutrition because she is aware of the influence food has on dental health. Reducing sugary snacks and adopting a nutrient-dense diet strengthens teeth against bacterial attacks.
Keep Up to Date:
Dr. Chamria believes that patients should keep up to date on developments in oral health. People are better equipped to make educated decisions regarding their oral health when they are aware of the most recent treatment and preventive strategies.
Conclusion
With a newfound understanding of the interplay between dental caries and plaque, we say adieu to the underworld of your mouth and remind you that maintaining good oral health is a lifelong struggle. As long as you maintain a strict dental hygiene regimen and have Dr. Chirag Chamria on your side, you should be able to handle any obstacles that life throws at you. May your smile be a ray of hope in the never-ending story of dental health.
Additional Resource
Links to Dr. Chirag Chamria’s Resources
Dr. Chirag Chamria’s Website:
Check out the informative posts, articles, and updates on oral health on Dr. Chamria’s official website. The website acts as a central location for materials that can help with comprehending and upholding the best possible dental hygiene.
Dr. Chirag Chamria on Instagram:
Follow Dr. Chirag Chamria on Instagram to receive updates on the newest developments in dentistry as well as bite-sized advice and visual guides. For daily inspiration on dental health, follow @drchiragchamria.