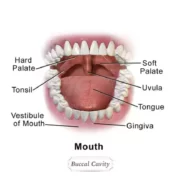
Dental caries, also known as tooth decay or cavities, is the result of a process called acidogenic decay. Bacteria in dental biofilm produce lactic acid when they break down carbohydrates like sugars. The lactic acid has a lowering effect on the pH in the mouth and causes demineralisation of the teeth. If left untreated, this process may cause destruction of the tooth enamel, which can only be reversed with professional help. A diet high in sugars and simple carbohydrates is considered the main risk factor for developing dental caries. While some people are more prone to develop it than others, there are also people who are immune to get caries as well as others that reduce their risk.
Enamel Thinning Variant
The enamel thinning variant (ET) has been associated with dental caries. This variant is an example of gene-environment interaction, where the environment affects the phenotype of the individual. In this case, the environment is dental caries that leads to thinning of the enamel. The enamel thinning variant inhibits the production of collagen that leads to thinner enamel. As a result, dental caries penetrates the enamel more easily.
Enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body. It is also the most mineralized tissue in the human body. Therefore, it is important to maintain its structure in order to prevent dental caries. The enamel thinning variant affects this structure and makes teeth more prone to dental caries. This variant is the most common one in the human population.
The risk of Dental Caries
The risk of caries variant (Risk) is another example of gene-environment interaction. This variant increases the risk of dental caries and is associated with weak cementum, the tissue that attaches the teeth to the bone in your jaw. Risk is caused by a deletion in the COL2A1 gene, which codes for collagen type II.

Type II collagen is critical for the formation of cementum, therefore, it can be concluded that the deletion in the COL2A1 gene leads to weaker cementum and is responsible for dental caries. The risk of caries variant can be treated with fluoride treatments. This variant is more common in people of Asian descent, which may be linked to the history of sugar cane cultivation in that region.
Pro-Inflammatory Gene Variant
The pro-inflammatory gene variant (Pro-inflammatory) is associated with a low risk of tooth decay. This gene variant is linked to the production of a protein called lipocalin-2. Lipocalin-2 is an anti-inflammatory protein that is important for the immune system. This gene variant has also been associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and other inflammatory diseases. People with this variant may have a better diet because they are less likely to develop it. This could also be linked to the lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
Bacteriologist Gordon E. Green of Detroit’s Henry Ford Hospital told the American Dental Association last week that about 1% of the adult population, regardless of racial origin, seems to be completely immune to tooth decay.
Conclusion to Dental Caries
Tooth decay is a process that has long been associated with the risk of dental caries. However, not all people have the same risk. Several genome-wide association studies have identified several genetic variants that are associated with dental caries (e.g., enamel thinning variant, risk of variant, and pro-inflammatory gene variant). These variants illustrate the importance of gene-environment interaction in dental health.