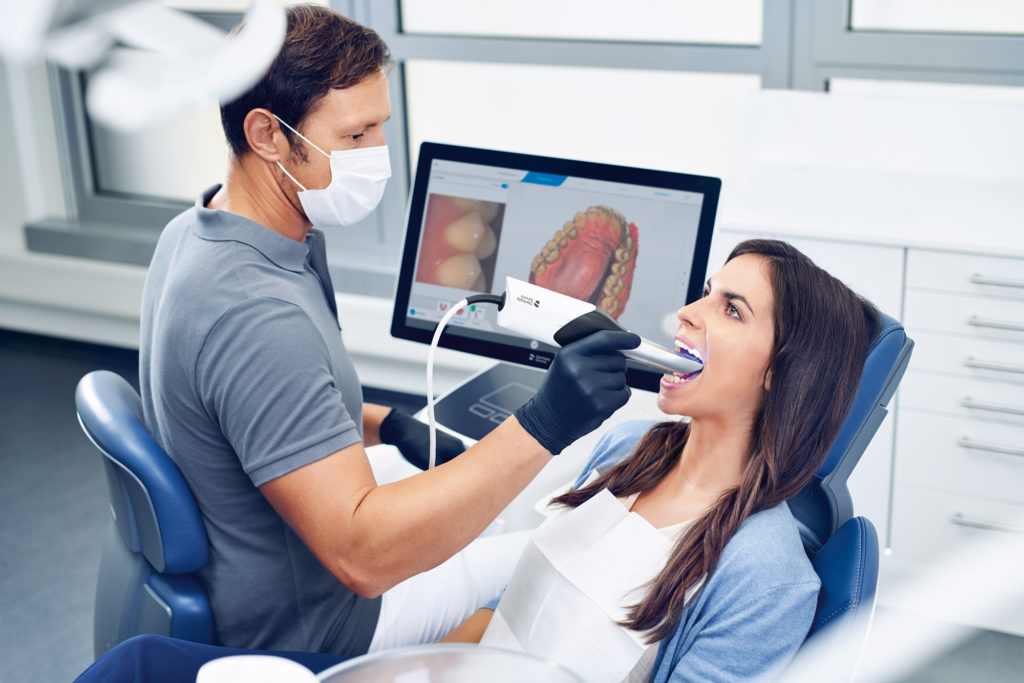
Have you ever wanted to explore the differences between alginate and intraoral impressions? Are you curious about the contrasts between these two dental materials? For dental professionals and patients alike, discovering the contrasts between alginate and intraoral impressions can be an eye-opening experience. Alginate and intraoral impressions are two of the most widely used dental materials, and understanding the differences between them can have a huge impact on the quality of care you provide. In this article, we’ll explore the contrasts between alginate and intra-oral impressions, and discuss why it’s important to be aware of their differences.
What is an Alginate Dental Impression?
Alginate impressions are made from a combination of seaweed and gypsum, which are combined to form an elastic substance. This material is then spread over a prepared surface, such as the mouth, and allowed to be set. This creates a negative image of the mouth, which is then used to make a custom dental restoration. Alginate impressions are generally used for crowns, bridges, and dentures. The Alginate impressions are also often used for orthodontic appliances, as the material is flexible and can be used to create a more accurate representation of the patient’s teeth and gums.
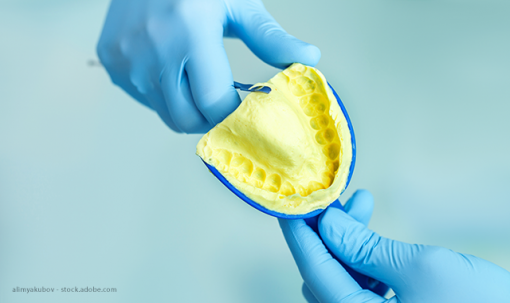
Putty impressions are highly accurate, as the material can be manipulated to capture even the tiniest details of the patient’s mouth. The material also has a short setting time, which means that impressions can be made quickly and easily. Alginate impressions are also relatively inexpensive, making them a cost-effective option for many dental practices.
What is an Intra-oral dental Impression?
Intraoral impressions are made with a different type of material than alginate impressions. Intraoral impressions are usually made with a silicone-based material, which is injected into the mouth to create a negative image of the patient’s teeth and gums. Like alginate impressions, intra-oral impressions are highly accurate and can capture even the finest details of the patient’s mouth. Intraoral impressions are often used for dental crowns, bridges, and dentures, as well as orthodontic appliances and other types of restorations.
Unlike alginate impressions, intra-oral impressions require more time and skill to create. The material must be mixed and injected into the mouth and then allowed to set. This process takes longer than creating an alginate impression, but the resulting impression is much more accurate and detailed. Intra-oral impressions are also more expensive than alginate impressions, making them a less option for many dental practices.

An intra-oral impression is a dental procedure in which a three-dimensional replica of a patient’s teeth and gums is created using a dental impression material. This replica is used to create a model of the patient’s teeth and gums, which is then used to design and create dental restorations such as crowns, bridges, or dentures.
During the intraoral impression procedure, a dental impression material such as alginate or silicone is placed in a tray and then placed in the patient’s mouth. The patient is instructed to bite down on the tray, which creates an impression of their teeth and gums. The impression material is then allowed to set, and the tray is removed from the mouth.
The impression is then sent to a dental laboratory, where it is used to create a model of the patient’s teeth and gums. This model is used to design and create the dental restoration that will be fitted to the patient’s teeth.
Intraoral impressions are an important part of many dental procedures, as they provide an accurate and detailed replica of a patient’s teeth and gums that can be used to create precise and well-fitting dental restorations. They are also used in orthodontics to create custom braces or aligners.
Differences between Alginate and Intra-oral Dental Impressions
While alginate and intra-oral impressions are both used to create accurate images of a patient’s teeth and gums, there are several key differences between the two materials. The most obvious difference is the material used to create the impressions – alginate impressions are made with a combination of seaweed and gypsum, while intraoral impressions are made with a material.
The techniques used to create alginate and intra-oral impressions are also different. Putty impressions are created by spreading the material over a prepared surface and allowing it to set, while intra-oral impressions require the material to be mixed and injected into the mouth.
In addition, the accuracy and detail of alginate and intraoral impressions can vary. Alginate impressions are generally more accurate than intraoral impressions, as the material can be manipulated to capture even the tiniest details of the patient’s mouth.
Material composition: Alginate is a water-based impression material that is derived from seaweed, while intra-oral dental impression materials are typically silicone-based.
Setting time: Alginate sets more quickly than most intra-oral dental impression materials, usually within one to two minutes. In contrast, some intra-oral dental impression materials can take up to five minutes or more to set.
Accuracy: While both alginate and intra-oral dental impressions are capable of producing accurate replicas of a patient’s teeth and gums, intra-oral dental impressions are generally considered to be more accurate due to their ability to capture more detail and finer features of the teeth and gums.
Shelf life: Alginate has a relatively short shelf life and must be used within a few weeks of being mixed, whereas many intra-oral dental impression materials have a longer shelf life and can be stored for several months before use.
Cost: Alginate is generally less expensive than most intra-oral dental impression materials, which can be more expensive due to their higher accuracy and longer shelf life.
Properties of Alginate Dental Impression Material
Alginate impression material is a combination of seaweed and gypsum, which is mixed together to form an elastic substance. This material is then spread over a prepared surface and allowed to set, creating a negative image of the patient’s mouth. Alginate impression material is highly accurate and can be manipulated to capture even the tiniest details of the patient’s mouth. It is also relatively inexpensive and has a short setting time, making it a popular choice for many dental practices.
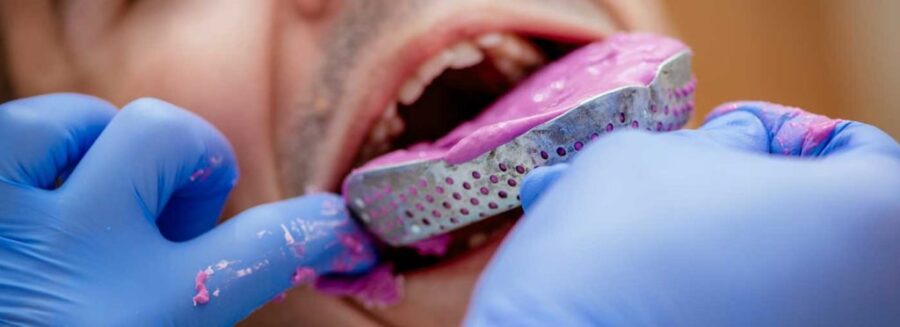
Putty impression material is also relatively flexible, which allows it to capture the shape and texture of the patient’s teeth and gums more accurately than some other dental materials. It is also easy to use, as it can be spread over a prepared surface with minimal effort.
Properties of Intra-oral Dental Impression Material
Intraoral impression material is usually made with a silicone-based material, which is injected into the mouth to create a negative image of the patient’s teeth and gums. Unlike alginate impression material, intraoral impression material has a longer setting time and is more expensive. However, its accuracy and detail are superior to alginate impressions, as it can capture the shape and texture of the patient’s teeth and gums more accurately.
Intraoral impression material is also more flexible than alginate impressions. Which allows it to capture even the slightest details of the patient’s mouth. It is also relatively easy to use, as the material can be injected into the mouth with minimal effort.
Benefits of Alginate Dental Impression Material
Alginate impression material has several benefits that make it a popular choice for many dental practices. As mentioned above. The impression material is relatively inexpensive and has a short setting time. Making it a cost-effective option for many practices. It is also highly and can capture even the tiniest details of the patient’s mouth. Additionally, the alginate impression material is relatively flexible. Which allows it to capture the shape and texture of the teeth and gums more accurately than some other dental materials.
Benefits of Intra-oral dental Impression Material
Intra-oral impression material also has several benefits that make it a popular choice for many dental practices. As mentioned above, the intraoral impression material is more accurate and detailed than alginate impressions. It is also more flexible, which allows it to capture even the slightest details of the patient’s mouth. Additionally, the intraoral impression material is relatively easy to use. As the material can be injected into the mouth with minimal effort.
Techniques for Using Alginate and Intraoral Impression Materials
Creating alginate impressions requires spreading the material over a prepared surface and allowing it to set. This process is relatively easy and can be done quickly. Intraoral impressions, on the other hand, require the material to be mixed and injected into the mouth. Which takes longer and requires more skill.
When creating either type of impression. It is important to ensure that the material is spread evenly and that the impression is as accurate and detailed as possible. Additionally, it is important to allow the material to be set for the recommended amount of time before removing it.
Conclusion
Alginate and intraoral impressions are two of the most widely used dental materials. And understanding the differences between them can have a huge impact on the quality of care you provide. A Alginate impressions are made with a combination of seaweed and gypsum. While intraoral impressions are made with a silicone-based material. Alginate impressions are generally more accurate than intraoral impressions. But intra-oral impressions are more detailed and can capture the shape and texture of the patient’s teeth and gums more accurately. When using either type of impression material. It is important to ensure that the material is spread evenly and that the impression is as accurate and detailed as possible. Additionally, it is important to allow the material to be set for the recommended amount of time before removing it.