We explore the potential of this restorative method and go into the area of post- and core-restoration in this complete instruction on Resin as a Luting Agent. By providing a long-lasting and aesthetically acceptable solution for many dental restorations, resin luting has revolutionized the profession of dentistry. We examine the science underlying resin luting and how it improves the durability and stability of post and core restoration, from its beginnings to the most recent developments. With the information in this article, you will have a clear road map to understanding resin luting and its uses.
What is a Luting Agent?
A luting agent is a crucial in dentistry designed to bond dental restorations, such as crowns, bridges, inlays, onlays, and dental prostheses, to natural teeth or implants. Functioning as a reliable adhesive, the primary purpose of a luting agent is to establish a durable connection between the restoration and the tooth structure. This not only ensures the restoration’s stability but also involves creating a seal at the interface to prevent leaks and bacterial infiltration. The long-term success and durability of dental restorations hinge significantly on the effectiveness of luting agents.
What does a Resin Luting Agent do?
Dental materials are used to glue or cement dental restorations to real teeth or dental implants, such as crowns, bridges, inlays, onlays, and veneers.
Advantages of Resin for Post and Core Procedure
Resin materials are capable of forming a solid bond with both the tooth structure and the post, resulting in a connection that is both durable and dependable. It may be matched to a natural tooth’s colour and translucency for improved aesthetics.
Resin materials provide a tight seal, lowering the possibility of microleakage, which may cause supplementary problems like tooth rot. Resin-based posts and cores may provide enough strength to sustain the finished repair, guaranteeing long-term durability. Resin-based methods often enable more conservative tooth preparation, retaining more natural tooth structure.
Types of Resin Luting Agent
There are several varieties of resin-luting agents on the market, each with special qualities and attributes. Dental practitioners may choose the best resinluting agent for their unique clinical scenario by being aware of the many varieties.
Total-Etch Resin Luting Agent
Prior to the installation of the resin, an adhesive system must be applied to the tooth structure. The tooth surface is given micro-retentive characteristics during the etching process, which strengthens the binding between the resin and the tooth. Excellent bond strength is offered by total-etch resin luting agents, which are also appropriate for a variety of therapeutic applications.
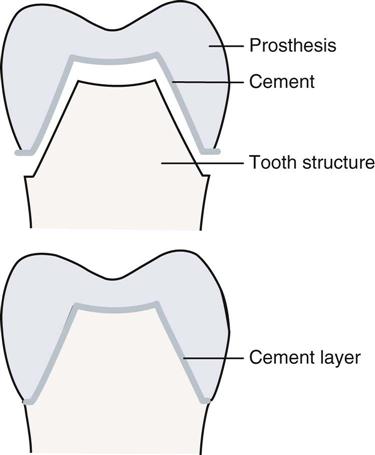
Dual-Cure Resin Luting Agent
These luting agents are flexible in many clinical settings since they can be both chemically and light-cured. Even in places like deep subgingival zones, where light curing may be difficult, dual-cure resin luting agents assure adequate polymerization. They are appropriate for situations with restricted access to light and provide dependable binding strength.
Self-Adhesive Resin Luting Agent
These luting agents combine the adhesive and luting components into a single substance, eliminating the need for additional adhesive systems. They are a popular option in several therapeutic settings because of their comfort and ease of use. However, it’s crucial to remember that they could not have as strong a connection as other resin luting agents.
Bonding mechanisms of Resin Luting Agents
The increased bond strength of resin-luting agents is attained by combining chemical and mechanical bonding processes. When employing resin as a luting agent for post- and core treatments, dental practitioners may get the best outcomes by being aware of these bonding processes. The creation of a strong link between the resin and the tooth structure is a key component of the chemical bonding process of resin luting agents.
The adhesive system that is applied to the tooth surface in total-etch and self-etch resin luting agents comprises acidic monomers that etch the enamel and dentin and produce micro-retentive characteristics. These characteristics make it possible for the resin and tooth structure to mechanically lock together, strengthening the connection.
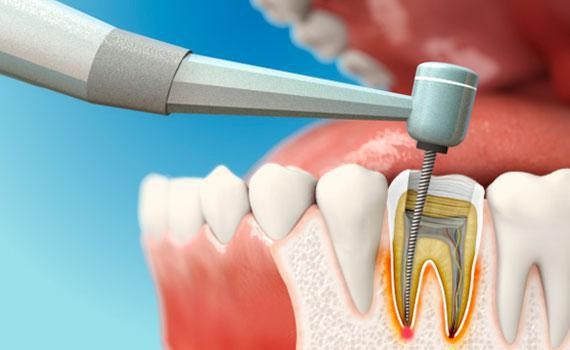
Step-by-Step Procedure
Preparing the tooth for the post and core restoration comes first. Ensure a clean and strong foundation for the repair by removing any degradation or restorations that already exist.
Based on the clinical scenario, choose the right post size and material. Make sure that the post is passively seated and fits properly into the root canal. Depending on the resin-luting agent you choose, use a system of adhesive that is appropriate.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for applying the proper etchant to the tooth structure when using a total-etch or self-etch resin luting agent. Thoroughly rinse and dry the tooth, leaving a wet area for the application of the glue.
Follow the manufacturer’s directions for using the adhesive system. Make sure the post surface and tooth structure are completely covered. Utilizing the suitable curing light, light-cure the glue.
Spray the post surface with the resin-luting agent, making sure it is evenly distributed. After inserting the post and removing any extra resin, seal the root canal. As directed by the manufacturer, light-cure the resin.
Use an appropriate restorative substance to complete the core buildup once the resin luting agent has completely cured. For both functional and esthetic success, make sure the shape and occlusal alignment are correct.
To create a smooth and natural-looking surface, finish and polish the repair. Pay close attention to interproximal and occlusal contacts to guarantee the patient’s comfort and good function.
Give the patient the essential post-operative instructions, including recommendations for dental hygiene and any necessary safety measures.
Comparison of Resin Luting Agents with other Materials
Composite Cement
Since both composite cement and resin-luting agents are resin-based, they have certain similarities. But in difficult clinical circumstances, composite cement may not provide the same bond strength as resin-luting agents.
Better control over the shade and translucency is possible with resin-luting agents, resulting in a more appealing and natural restoration.
Zinc Phosphate Cement
Resin-luting agents provide better bond strength and cosmetic outcomes as compared to zinc-phosphate cement.
The link between the post and core repair is weaker because zinc phosphate cement depends on mechanical retention rather than resin’s adhesive qualities.
Additionally, resin luting agents provide higher translucency and shade matching, improving the final aesthetic result.
Long-term Success Rates and Clinical Outcomes
Studies have demonstrated that when used as luting agents for post- and core treatments, resin luting agents may provide great long-term success rates and positive clinical results. Let’s look at some of the results of the study in this field.
The survival rates of post- and core restorations bonded with resin-luting agents were studied in a systematic review and meta-analysis that was published in the Journal of Dentistry in 2023. Studies with follow-up periods ranging from one to five years were included in the review. The findings revealed that resin-luting agents had a 94.2% total survival rate, which is very successful and long-lasting.
Conclusion
The use of resin-luting agents in post- and core-procedures has several benefits. They are a great option for creating dependable and visually acceptable restorations because of their exceptional bonding qualities, aesthetic appeal, and adaptability. Resinluting agents are anticipated to become more and more important in post- and core operations as the discipline of dentistry develops. We really hope that our effort was beneficial to you.