The human body is a complex and integrated system. And it is becoming increasingly clear that the health of our hearts is closely linked to the health of our mouths. Recent research has shown that periodontitis. Or gum disease can have a direct effect on the risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack and stroke. This connection between periodontitis and heart disease is now being unveiled. As more and more evidence is gathered showing the wide-reaching implications of poor oral health. This article will explore the connection between periodontitis and heart disease, and how the two are linked.
What is Periodontitis?
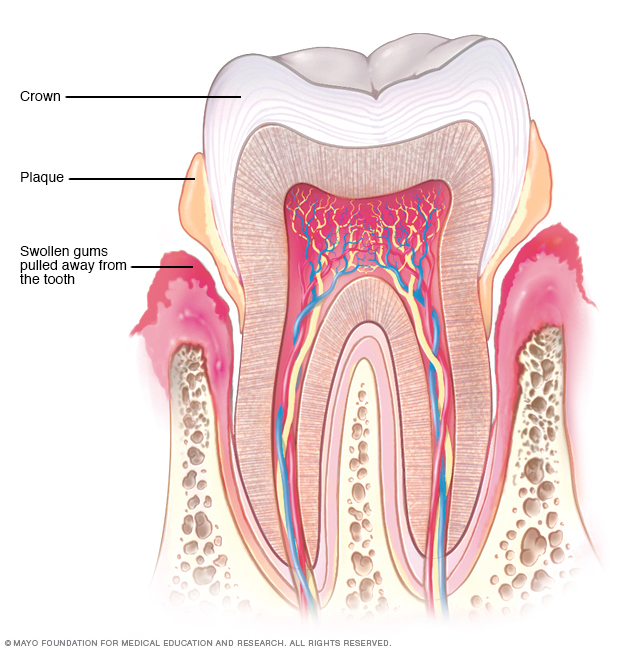
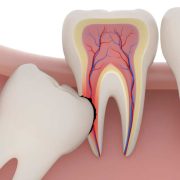
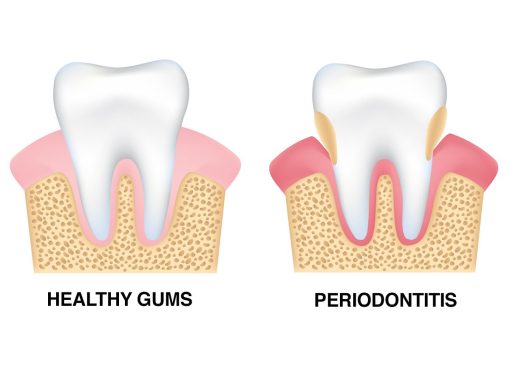
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the gums, caused by bacteria in the mouth. The disease occurs when bacteria in plaque form on the teeth and gums. And the body’s immune system responds by attacking the infection. This can lead to inflammation of the gums, which can cause redness, swelling, and bleeding. If left untreated, periodontitis can cause the destruction of the connective tissues and bone that support the teeth, resulting in tooth loss.
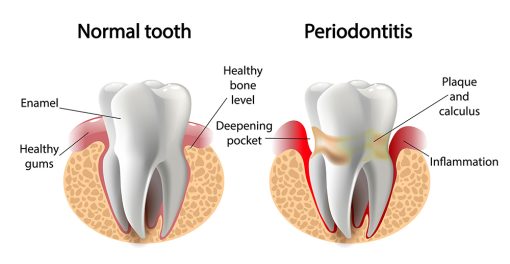
It is estimated that up to 10% of adults in the United States suffer from some form of periodontitis, making it one of the most common oral health problems. While periodontitis is largely preventable, it can be difficult to diagnose in its early stages, as the symptoms may be mild. A dentist or periodontist will use x-rays and other imaging techniques to look for signs of the disease.
How does Periodontitis affect the Heart?
Recent research has shown that periodontitis can have a direct effect on the risk of cardiovascular disease. This connection is thought to be due to the bacteria in periodontitis entering the bloodstream and traveling to the heart, where they can cause inflammation and damage to the heart’s blood vessels. This can lead to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
In one study, researchers found that individuals with gum disease were 2.7 times more likely to suffer from a heart attack than those without the disease. Another study found that individuals with periodontitis were 2.5 times more likely to suffer from a stroke than those without the disease.
Risk Factors for Periodontitis and Heart Disease
While periodontitis is largely preventable, there are certain risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing the disease. These risk factors include smoking, diabetes, certain medications, and certain genetic factors. Additionally, individuals who have poor oral hygiene, such as not brushing or flossing regularly, are more likely to develop periodontitis.
It is important to note that while these risk factors can increase the risk of developing periodontitis, they can also increase the risk of developing heart disease. For example, smoking is known to be a risk factor for both periodontitis and heart disease, and individuals with diabetes are more likely to develop both conditions.
Role of Genetics in Periodontitis and Heart Disease
It has been shown that genetics can play a role in the development of periodontitis and heart disease. Certain genetic factors can increase the risk of developing both conditions, and it has been found that individuals with certain genetic variants are more likely to suffer from both gum and heart disease. In addition to genetic factors, a certain lifestyle, and environmental factors can also increase the risk of developing both periodontitis and heart disease.
There is evidence to suggest that periodontitis, a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and destroys the bone that supports teeth, may be linked to an increased risk of heart disease. The theory is that the bacteria that cause periodontitis can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body, including the heart. Once in the heart, these bacteria can cause inflammation, which can lead to the development of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and atherosclerosis.
The Link Between Periodontitis and Stroke
A stroke is a type of cardiovascular event that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted. A stroke can lead to serious complications and can even be fatal. Recent research has shown that periodontitis can increase the risk of stroke. In one study, individuals with periodontitis were 3.2 times more likely to suffer from a stroke than those without the disease.
The link between periodontitis and stroke is thought to be due to the bacteria in periodontitis entering the bloodstream and traveling to the brain, where they can cause inflammation and damage to the blood vessels in the brain. This can lead to an increased risk of stroke.
Nutrition plays an important role in the prevention and management of periodontitis and heart disease. Eating a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. And avoiding processed and sugary foods can help to reduce the risk of both conditions. Additionally, avoiding smoking and drinking alcohol in moderation can also help to reduce the risk of periodontitis and heart disease.
Role of Nutrition in Periodontitis and Heart Disease
In addition to a healthy diet, it is also important to maintain good oral hygiene. Brushing and flossing regularly can help to reduce the buildup of plaque on the teeth and gums. Which can lead to periodontitis. Additionally, regular dental check-ups can help to identify any signs of periodontitis and can help to keep the disease from progressing.
Several studies have shown a link between gum and heart disease, although the exact nature of this relationship is still being researched. Some studies have found that people with periodontitis are at a higher risk of developing heart disease than those without periodontitis, while others have found that treating periodontitis can improve heart health.
While the link between periodontitis and heart disease is not fully understood, it is clear that maintaining good oral health is important for overall health and well-being. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings can help prevent periodontitis and other oral health problems and may also help reduce the risk of heart disease.
Treatment Options for Periodontitis and Heart Disease
If periodontitis is detected, it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible. The most common treatment for periodontitis is a deep cleaning called scaling and root planing. This procedure removes plaque and tartar from the teeth and gums and can help to reduce the inflammation associated with periodontitis.
In addition to scaling and root planing, other treatments for gums disease include antibiotics, laser therapy, and surgery. It is important to note that these treatments may not be effective in all cases. And it is important to speak to a dentist or periodontist to determine the best course of treatment.
For individuals with heart disease, treatments such as lifestyle modifications, and medications are. And surgery can help to reduce the risk of complications. It is important to speak to a doctor to determine the best course of treatment for an individual’s situation.
How to Prevent Periodontitis and Heart Disease
The best way to prevent periodontitis and heart disease is to maintain good oral hygiene and a healthy lifestyle. Brushing and flossing regularly, and eating a balanced diet. Avoiding smoking and drinking alcohol in moderation, and getting regular dental check-ups can all help to reduce the risk of both conditions. Additionally, individuals should be aware of their risk factors for periodontitis and heart disease and seek treatment as soon as possible if any symptoms are detected.
Conclusion
The connection between gum disease and heart disease is becoming increasingly clear. As more and more evidence is gathered showing the wide-reaching implications of poor oral health. By understanding the connection between the two conditions. We can take steps to protect ourselves and our families from the risks associated with poor oral health. By good oral hygiene, and eating a balanced diet. Avoiding smoking and drinking alcohol in moderation, and getting regular dental check-ups. We can reduce our risk of both and heart disease.